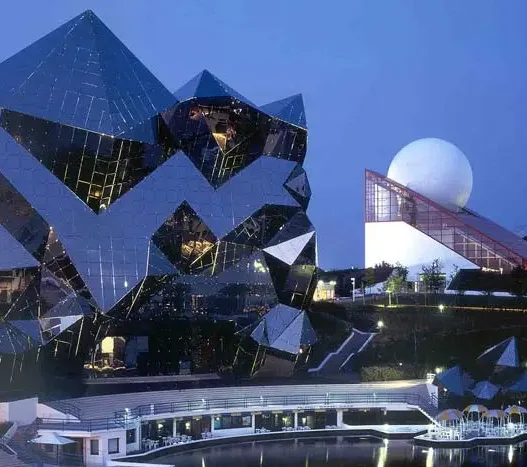
Soviet Modernism represents a fascinating chapter in the history of architecture, characterized by bold designs and a unique blend of ideology and aesthetics. This early twentieth-century architectural movement sought to reflect the ambitions of the new socialist state. The influence of Soviet Modernism can be felt in Moscow, and many buildings still stand as a testament to that era.

Historical Context
To understand Soviet Modernism, we must first consider the turbulent historical background of Russia in the early 20th century. Following the Russian Revolution of 1917, the country underwent a major transformation in an effort to build a new society based on socialist principles. This change required the redesign of urban spaces and prompted architects to break with traditional styles and embrace modernism. The 1920s and 1930s saw an influx of avant-garde ideas, with architects such as the constructivists attempting to combine art and utility to create functional yet visually striking buildings.
Key Features
Soviet Modernism is distinguished by several distinctive features that reflect the ideological underpinnings of the period. The use of geometric shapes, sharp lines and the absence of ornamentation summarize the movement’s embrace of functionality over frivolity. Buildings often incorporated materials such as concrete and glass, symbolizing progress and industrial power. Designs were intended to convey a sense of collective identity, with communal spaces playing a vital role. This architectural language conveyed the ideals of the state, emphasizing the importance of community and common purpose.
Influential Architects
Many architects played important roles in shaping Soviet Modernism. One of them is Moisei Ginzburg, whose work epitomizes the constructivist ethos. His design for the Narkomfin Building introduced innovative ideas about communal living and the integration of individual and collective needs. Another important architect, Konstantin Melnikov, is famous for his unique, often avant-garde designs, such as the Melnikov House, which reflect both modernist principles and his personal artistic vision. These architects and their contemporaries not only transformed Moscow’s skyline, but also influenced architectural practice around the world.
Impact on Urban Development
The impact of Soviet Modernism on urban development in Moscow is profound. Large-scale housing projects such as Khrushchyovkas emerged in response to the post-war housing crisis. These prefabricated concrete apartment buildings were intended to efficiently house the growing urban population. Furthermore, public buildings, such as Moscow Metro stations, exemplify the grandeur of the movement, blending functionality with artistic expression. This urban planning not only met immediate needs, but also shaped the identity of the city, creating spaces that encouraged social interaction and participation.
The Legacy of Soviet Modernism
Today, the legacy of Soviet Modernism is the subject of both admiration and criticism. While many of the original buildings face challenges such as neglect and modernization pressures, their historical and architectural significance is increasingly appreciated. Contemporary architects in Moscow are increasingly looking to this period for inspiration, re-imagining Soviet designs in new contexts. The interplay between the preservation of historic architecture and the adoption of modern design creates a dynamic urban landscape that reflects the complexity of Moscow’s past and its aspirations for the future.
Soviet Modernism remains a vital part of Moscow’s architectural narrative, offering insights into the ambitions, struggles and innovations of a bygone era. As the city evolves, the conversation around these structures continues, ensuring that their stories are not only remembered but also celebrated in the context of contemporary design.
A city steeped in history, Moscow is a fascinating tapestry of architectural styles that reflect its turbulent past and evolving present. Among the most significant influences on the city skyline is Soviet Modernism, a movement that emerged in the early to mid-20th century. This architectural style sought to embody the ideals of socialism while embracing new technologies and materials. Today, as Moscow continues to grow and modernize, remnants of Soviet architecture stand alongside contemporary designs, creating a unique blend of old and new. This exploration examines some of the most iconic examples of Soviet Modernist architecture that shaped the city.
Iconic examples of Soviet Modernist architecture
Soviet Modernism is characterized by its bold forms, monumental scale and often utilitarian design. Each building tells the story of an era when architecture was not only about aesthetics, but also about ideology and functionality. Among these, a few examples stand out, demonstrating the ambition and vision of the period.
Palace of the Soviets
Once intended to be the tallest building in the world, the Palace of Soviets was intended to be a great symbol of Soviet power and ideology. Designed in the 1930s, this colossal structure was to have a huge statue of Lenin at the top of its dome overlooking the city. Although construction was halted during the Second World War, the site remains a powerful reminder of the ambitions of the Soviet regime. Today the site is home to the Cathedral of Christ the Savior, rebuilt after being demolished to make way for the Palace. This juxtaposition of the aspirations of the past and the realities of the present underscores the ongoing dialogue between history and modernity in Moscow.
VDNH Exhibition Center
VDNH, or Vystavka dostizheniy narodnogo khozyaystva, is a large exhibition center that emerged in the 1930s. Designed to showcase the achievements of Soviet agriculture and industry, its pavilions are adorned with ornate sculptures and mosaics reflecting the artistic style of the period. The center’s architecture blends functionality with grandeur, creating an environment where culture and commerce intersect. Today, VDNH has evolved into a vibrant public space that hosts exhibitions, festivals and events and embodies the spirit of innovation it was originally built to celebrate.
House on the Quay
Overlooking the Moskva River, the House on the Quay is a striking example of Soviet architecture completed in the early 1930s. Originally designed as a residence for the elite of the Communist Party, it offers a blend of functionality and grandeur. The building’s long, linear form is punctuated by large windows, allowing for an abundance of natural light. The house became emblematic of the social aspirations of the time, housing not only apartments but also communal spaces that fostered a sense of community among its residents. Today, it stands as a testament to the complex relationship between architecture and politics, representing both privilege and the collective spirit of the times.
Seven Sisters
The Seven Sisters, a group of skyscrapers built in the Stalinist style, dominate Moscow’s skyline. Completed between the 1940s and 1950s, these buildings were designed to reflect the power and stability of the Soviet state. Blending Gothic and Baroque influences with Soviet ideals, each sister has its own unique characteristics. They serve as both functional spaces and national symbols, housing universities, hotels and government offices. As Moscow continues to modernize, the Seven Sisters remain a proud reminder of the city’s historical narrative and show how architecture can embody a nation’s identity.
Moscow Metro
The Moscow Metro is not just a transportation system; it is an architectural marvel that epitomizes Soviet Modernism. Opened in 1935, the stations are decorated with intricate mosaics, chandeliers and sculptures, turning each stop into a work of art. The design was intended to showcase the achievements of the Soviet Union and give its citizens a sense of pride. The Metro’s efficiency and beauty have made it a beloved part of everyday life in Moscow. As the city expands, the Metro continues to evolve, blending historical aesthetics with contemporary functionality to become a vital component of urban life in modern Moscow.
As a result, Moscow’s architectural landscape is a vivid reflection of its historical journey. Iconic examples of Soviet Modernism not only represent a specific era, but also continue to influence the city’s contemporary redesign. As Moscow moves forward, these structures provide vital links to the past, reminding us of the aspirations and challenges that made the city what it is today.
Contemporary Redesign Studies
Moscow’s architectural landscape is a mesmerizing tapestry woven with rich history and vibrant contemporary influences. As the city enters the 21st century, redevelopment efforts are reshaping the urban fabric, blending remnants of Soviet modernism with innovative designs that reflect current trends and needs. These initiatives are not just about aesthetics; they aim to improve the quality of life for residents while respecting the historic context of the city.
Overview of Redesign Initiatives
Redesign initiatives in Moscow have a dual focus: revitalizing public spaces and urban infrastructure while maintaining a dialogue with the city’s historic identity. As urbanization accelerates and populations grow, the need for functional, accessible and aesthetically pleasing environments has become paramount. Efforts are underway to transform idle spaces into vibrant centers for community interaction, commerce and culture. This evolution is marked by a commitment to sustainability through the incorporation of green spaces and environmentally friendly materials into new projects. By weaving contemporary elements into the historical narrative, these initiatives aim to create a city that honors its past while looking to the future.
Major Projects in Moscow
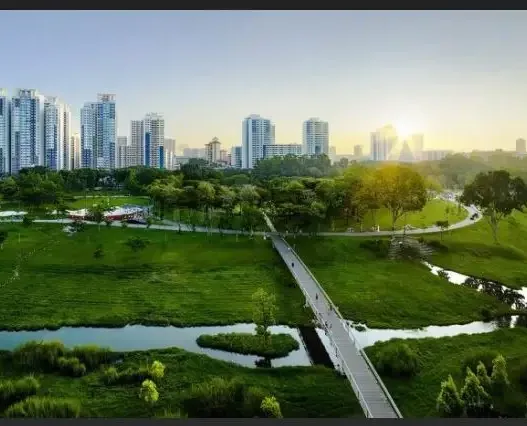
Several important projects exemplify contemporary redevelopment efforts in Moscow. Zaryadye Park, which opened near the Kremlin, is one notable example of these projects. This innovative park features a unique landscape design that combines a variety of natural environments, from wetlands to forests, and includes state-of-the-art architecture such as a floating bridge that offers spectacular views of the city. Another major project is the redevelopment of Gorky Park, which has been transformed into a cultural and recreational center, hosting art installations and public events. These projects not only enhance the aesthetics of the city, but also serve as public spaces that reflect the changing dynamics of urban life.
Balancing Preservation and Modernization
One of the most challenging aspects of Moscow’s redevelopment efforts is the balance between preservation and modernization. The city is home to numerous historic buildings and monuments that tell the story of its past. Designers and urban planners are faced with the complex task of integrating modern elements without overshadowing the historical significance of these spaces. This balance is crucial as it creates a sense of continuity, allowing residents and visitors to appreciate the city’s heritage while enjoying modern conveniences. Successful projects often involve adaptive reuse strategies where old structures are repurposed for contemporary use, creating a harmonious mix of old and new.
Community Engagement in Redesign
Community participation plays a vital role in the redevelopment process. Moscow’s redesign initiatives are increasingly involving local residents in discussions about their neighborhoods. Through workshops, public forums and design competitions, communities can voice their needs and preferences, ensuring that changes reflect the people who live there. This participatory approach not only fosters a sense of ownership among residents, but also results in designs that are more in line with the community’s identity and aspirations. By prioritizing local input, Moscow is adopting a more democratic approach to urban development.
Challenges for Designers
Despite the enthusiasm surrounding redesign efforts, designers face numerous challenges. Bureaucratic barriers, funding constraints and differing views among stakeholders can make projects difficult to plan and execute. Moreover, the need to address environmental concerns such as air quality and urban heat requires innovative solutions that may not always be feasible within existing frameworks. Moreover, the rapid pace of change brings with it the risk of gentrification, which can displace long-time residents and change the social fabric of neighborhoods. Designers must carefully navigate these complexities, seeking to create inclusive spaces that benefit all residents.
Ultimately, contemporary redesign efforts in Moscow represent a dynamic interplay between history and modernity. Through thoughtful initiatives that prioritize community engagement and sustainability, the city is envisioning a future that honors its past while embracing innovation. As these projects unfold, they promise to enrich the urban experience and make Moscow a vibrant and engaging place for future generations.
The Role of Sustainability in Architecture
Sustainability has become a central theme in architecture, shaping how we think about the built environment and its impact on the planet. In Moscow, the journey from Soviet modernism to contemporary redesign reflects a growing awareness of sustainability, blending historical context with innovative practices. Understanding this evolution helps us understand how architecture can address environmental challenges while enhancing urban life.
Sustainable Practices in Soviet Modernism
Soviet modernism in the early to mid-20th century was characterized by monumental buildings and functional design. Although sustainability was not a primary concern during its inception, some principles inadvertently aligned with sustainable practices. For example, the use of durable materials aimed to ensure longevity, reflecting the desire for permanence in a rapidly changing society. Buildings such as Moscow State University exemplify this approach by using robust materials that have stood the test of time.
Moreover, the Soviet emphasis on communal living encouraged a sense of shared space and resources. Housing projects such as the Narkomfin House included communal kitchens and shared facilities that encouraged efficient use of resources. Although not designed with sustainability in mind, these practices point to a collective way of living that aligns with modern sustainability ideals.
Modern Sustainable Design Approaches
Today, architects in Moscow are redefining the urban landscape with modern sustainable design approaches. This shift involves integrating environmentally friendly materials, advanced technologies and innovative design strategies. Architects are increasingly focusing on passive solar design, which maximizes natural light and reduces reliance on artificial heating and cooling. This technique is evident in projects such as Zaryadye Park, where the design blends in with its natural surroundings while minimizing environmental impact.
In addition, the use of green roofs and walls has also gained popularity. These features not only improve energy efficiency, but also enhance biodiversity in the urban fabric. The use of reclaimed materials is another feature of contemporary design, as architects strive to reduce waste and promote circular economy principles. Buildings like the Flacon Design Factory show how repurposed industrial spaces can be transformed into vibrant cultural hubs, demonstrating sustainability in action.
Green Spaces in Urban Planning
The integration of green spaces is vital for sustainable urban planning and offers numerous benefits that improve both environmental quality and the well-being of urban residents. In Moscow, urban designers are increasingly recognizing the importance of parks, gardens and green corridors. These spaces serve as vital lungs for the city, improving air quality and providing habitats for wildlife.
Gorky Park in Moscow, for example, has undergone significant transformations, transforming a neglected area into a vibrant public space that encourages community interaction. The redesign emphasized biodiversity and ecological balance, allowing native plant species to thrive. Urban green spaces also promote social cohesion, providing residents with a place to rest, socialize and engage in recreational activities, thereby improving the overall quality of life.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy efficiency is one of the cornerstones of sustainable architecture, which focuses on reducing energy consumption while maintaining comfort and functionality. In Moscow, architects are exploring innovative solutions to improve energy efficiency in both new construction and retrofitting of existing buildings. High-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows and the use of smart technologies play an important role in minimizing energy use.
For example, renovation of Soviet-era buildings often involves upgrading energy systems to meet modern standards. By implementing technologies such as smart meters and energy management systems, building owners can effectively monitor and reduce energy consumption. This approach not only reduces utility costs, but also contributes to broader environmental goals by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Redesign Case Studies
Several case studies in Moscow exemplify the successful integration of sustainability into architectural redesign. One notable example is the transformation of the former Red October Chocolate Factory into a creative space for arts and culture. This project preserved the historic façade while incorporating modern sustainable practices such as energy-efficient systems and green roofs.
Another example is the renovation of the VDNH (Vystavka dostizheniy narodnogo khozyaystva), which has become an important cultural and exhibition center. The redesign emphasizes accessibility and sustainability with extensive landscaping and energy-efficient buildings that host a variety of public events.
These case studies show how sustainable redesign can breathe new life into historic buildings and address contemporary environmental challenges. They highlight the potential of architecture to create spaces that are not only functional, but also enrich the urban experience and promote ecological balance.
In conclusion, the role of sustainability in architecture reveals the dynamic interplay between history and innovation, particularly in Moscow’s transition from Soviet modernism to contemporary redesign. As the city continues to evolve, the adoption of sustainable practices will be crucial in shaping a resilient and vibrant urban future.
The Cultural Significance of Architecture in Moscow
Architecture in Moscow serves as a powerful lens through which the city’s cultural, political and social narratives unfold. From the grandiose structures of the Soviet era to the sleek lines of contemporary design, each building tells a story of its time, reflecting the ideologies and aspirations of its creators. This rich architectural tapestry not only shapes the visual landscape of Moscow, but also influences the identity and experience of its residents and visitors.
Architecture as a Reflection of Ideology
Moscow’s architectural landscape has always been intertwined with the dominant ideologies of the time. During the Soviet era, architecture became a vehicle for expressing the ideals of socialism. Monumental structures such as the Seven Sisters, which dominate the skyline, were designed to showcase the power and progress of the state. Their lofty forms and intricate details symbolize the strength and resilience of the Soviet Union, while also serving practical purposes as residential and administrative buildings.
In contrast, contemporary architecture in Moscow often reflects a more individualistic approach, adapting to global trends and the complexities of modern life. New developments such as Zaryadye Park and the Vostok Tower embrace innovative designs that prioritize sustainability and public engagement. They represent a shift in ideology, where the focus shifted from displaying state power to celebrating community and environmental awareness.
Public Perception of Soviet Buildings
The perception of Soviet-era architecture among Muscovites is multifaceted. For many, these buildings evoke nostalgia for a time when the city was perceived as a bastion of innovation and ambition. But this admiration is often mixed with criticism. While some see the monumental designs as oppressive relics of a bygone regime, others appreciate their historical significance and the artistry of their creation.
Public opinion varies widely, with younger generations sometimes seeing these structures as outdated, while older citizens may see them as symbols of national pride. This ongoing dialog about the value of Soviet architecture contributes to a broader understanding of Moscow’s identity and architectural heritage. As the city comes to terms with its past while trying to create a vibrant future, it raises important questions about conservation and modernization.
The Impact of Architecture on Identity
Architecture plays an important role in shaping the identity of Moscow and its residents. Dominated by both Stalinist structures and modern glass facades, the skyline reflects the city’s dynamic history and its prospects for the future. Each building contributes to a collective memory, influencing how people perceive their environment and themselves within it.
Moreover, the interaction between old and new architecture fosters a sense of continuity and change. For example, the construction of new buildings as well as the restoration of historic sites creates a dialog between tradition and modernity. This fusion not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the city, but also strengthens a sense of belonging among its residents as they navigate a space that honors its past and embraces innovation.
Events and Exhibitions Celebrating Architecture
Moscow hosts a variety of events and exhibitions celebrating its architectural heritage and contemporary innovations. The Moscow Architecture Biennale, for example, brings together architects, urban planners and enthusiasts from around the world to explore themes of urbanism, sustainability and social responsibility. These gatherings not only showcase groundbreaking design, but also stimulate debate about the future of urban life.
Exhibitions at key venues such as the Garage Museum of Contemporary Art highlight the intersection of architecture with art and culture, encouraging a deeper appreciation of the built environment. Such events provide a platform for local talent and international figures to interact with the public, stimulating curiosity and dialog about the role of architecture in shaping urban life.
The Role of Architecture in Tourism
Architecture is a major driver of tourism in Moscow, attracting visitors eager to explore its unique blend of historical and contemporary sites. Iconic buildings such as the Kremlin, St. Basil’s Cathedral and the Bolshoi Theater are not only architectural wonders, but also cultural symbols that attract millions of tourists every year.
In recent years, the revitalization of urban areas and the construction of modern attractions have further enhanced Moscow’s appeal. Projects such as the Moscow River Embankment and the redevelopment of Gorky Park have transformed public spaces into vibrant hubs for locals and visitors alike. These initiatives demonstrate how thoughtful architectural design can enhance the urban experience and increase civic engagement while promoting tourism.
In conclusion, the cultural significance of architecture in Moscow is deep and multifaceted. It reflects the ideologies of its time, shapes public perception, influences identity and contributes to the city’s role as a tourist destination. As Moscow continues to evolve, its architecture remains a vital element in telling the story of its past, present and future.
Future Directions of Moscow Architecture
Moscow stands at the intersection of history and innovation, and its architectural landscape is evolving rapidly. The legacy of Soviet Modernism, characterized by monumental structures and a unique aesthetic, is now intertwined with contemporary design philosophies. This fusion sets the stage for an exciting future marked by new trends, technological advances and a global perspective.
Emerging Trends in Design
Moscow’s architectural scene is increasingly embracing different styles that reflect both its rich history and its forward-looking vision. One prominent trend is the movement towards sustainability, where architects are prioritizing environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient buildings. This shift is not only a response to environmental concerns, but also a reflection of changing social consciousness. For example, projects such as the Flacon Design Factory show how adaptive reuse can breathe new life into former industrial spaces and transform them into vibrant cultural hubs.
Furthermore, the integration of public spaces is also gaining momentum. Architects are realizing the importance of creating shared spaces that encourage social interaction. This is evident in projects like Zaryadye Park, which seamlessly blends nature with urban life, offering Muscovites a green oasis in the middle of the bustling city. Such designs not only enhance the aesthetics of the city, but also promote a sense of community and well-being.
The Role of Technology in Architecture
Technology is revolutionizing the way architects approach design and construction in Moscow. Advanced software and modeling tools provide incredible precision and creativity, allowing architects to visualize complex structures before they come to life. For example, the use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) improves collaboration between stakeholders, streamlining the construction process and minimizing errors.
Moreover, smart building technology is becoming increasingly common. These innovations include automated systems that control lighting, heating and security, making buildings more efficient and user-friendly. An example of this can be seen in the Vostok Tower, where the latest technology ensures optimal energy use while providing a comfortable environment for building occupants. As technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly shape the future of Moscow’s architectural identity.
Prospects for Future Redesign Projects
Looking ahead, there are many exciting redevelopment projects on the horizon for Moscow. One key prediction is the continued transformation of the city’s riverside areas. As city planners seek to revitalize these areas, we can expect to see a mix of residential, commercial and entertainment facilities that prioritize accessibility and sustainability. Projects such as the Moscow River Embankment are paving the way for this vision and promise to increase public interaction with the waterfront.
Another expected trend is the proliferation of mixed-use developments. These projects are designed to create vibrant neighborhoods where people can live, work and play without being dependent on transport. By integrating residential, retail and office space, the architects are promoting a more interconnected urban environment. Such designs not only contribute to a more dynamic city, but also adapt to the needs of a modern population seeking comfort and community.
Impact of Global Architectural Trends
Moscow is not isolated in its architectural evolution; it is influenced by global trends that reflect broader shifts in design philosophy. The city is marked by the rise of biophilic design, which emphasizes the connection between man and nature. By incorporating natural elements into their designs, architects are creating spaces that promote health and well-being. This approach is evident in projects featuring green roofs, living walls and an abundance of natural light, contributing to a more harmonious urban experience.
In addition, the minimalist aesthetic popularized by architects around the world is gaining traction in Moscow. This style promotes simplicity and functionality, focusing on clean lines and open spaces. Buildings such as the new Tretyakov Gallery exemplify this trend, showing how minimalism can enhance appreciation of art and culture and provide a serene environment.
Attracting a New Generation of Architects
As Moscow’s architectural scene evolves, it is crucial to engage the next generation of architects. Educational institutions are adapting their curricula to incorporate contemporary design principles and sustainability practices, ensuring that students are equipped to meet future challenges. Workshops, competitions and collaborative projects with established firms encourage creativity and innovation among young designers.
Moreover, community participation is becoming a vital part of the design process. By encouraging public participation in architectural discussions, Moscow fosters a sense of ownership among its citizens. This inclusive approach not only enriches the design process, but also ensures that future projects align with the needs and desires of the community.
As a result, the future of Moscow’s architecture is like a tapestry woven from the rich history and vibrant threads of modern design. As new trends take shape, technology plays an important role in shaping these developments. With global influences in mind and determined to attract the architects of the future, Moscow is poised to become a beacon of architectural innovation that reflects the dreams and aspirations of its people.
Discover more from Dök Architecture
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.