The Bauhaus, a German art school founded by Walter Gropius in 1919, revolutionized design and left a lasting legacy that continues to influence the world of art, architecture and design today. Lasting only fourteen years, this influential movement challenged traditional aesthetics and embraced a new approach to design that prioritized functionality, simplicity and the integration of art and technology.
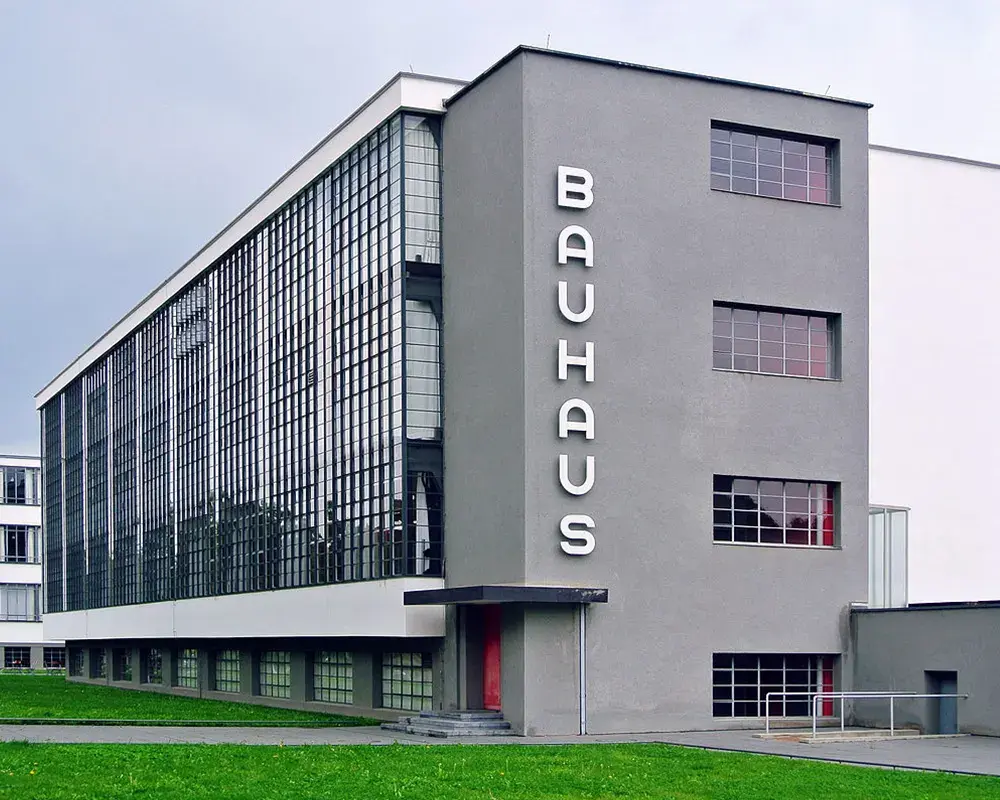

Bauhaus Movement and Its Impact on Design
The Bauhaus movement emerged after World War I, a period of significant social and cultural upheaval. It sought to create a new world order based on reason, functionality and social responsibility. The school’s core principles of “form follows function“, simplicity and mass production were a direct response to the excesses of the pre-war period.
Bauhaus adopted a holistic approach to design, encompassing architecture, furniture, textiles, ceramics and graphic design.
The movement’s focus on functionality and simplicity at its core led to the creation of iconic designs that are still admired today, such as Marcel Breuer‘s Wassily Chair and Mies van der Rohe‘s Barcelona Chair.
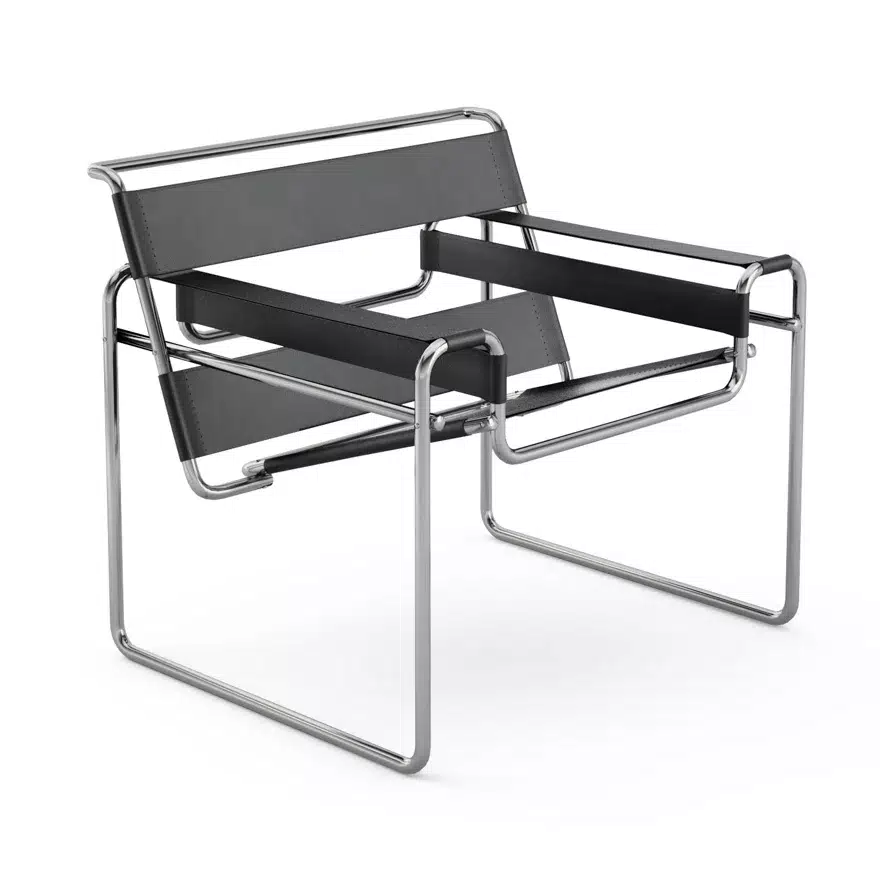
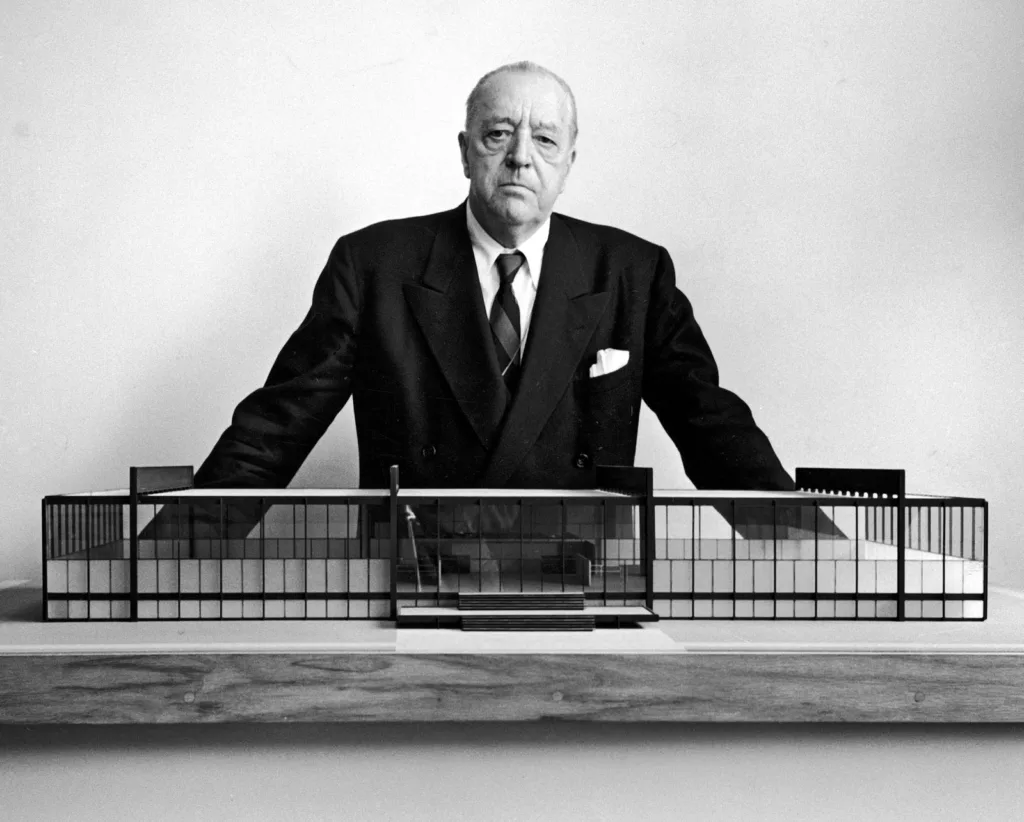
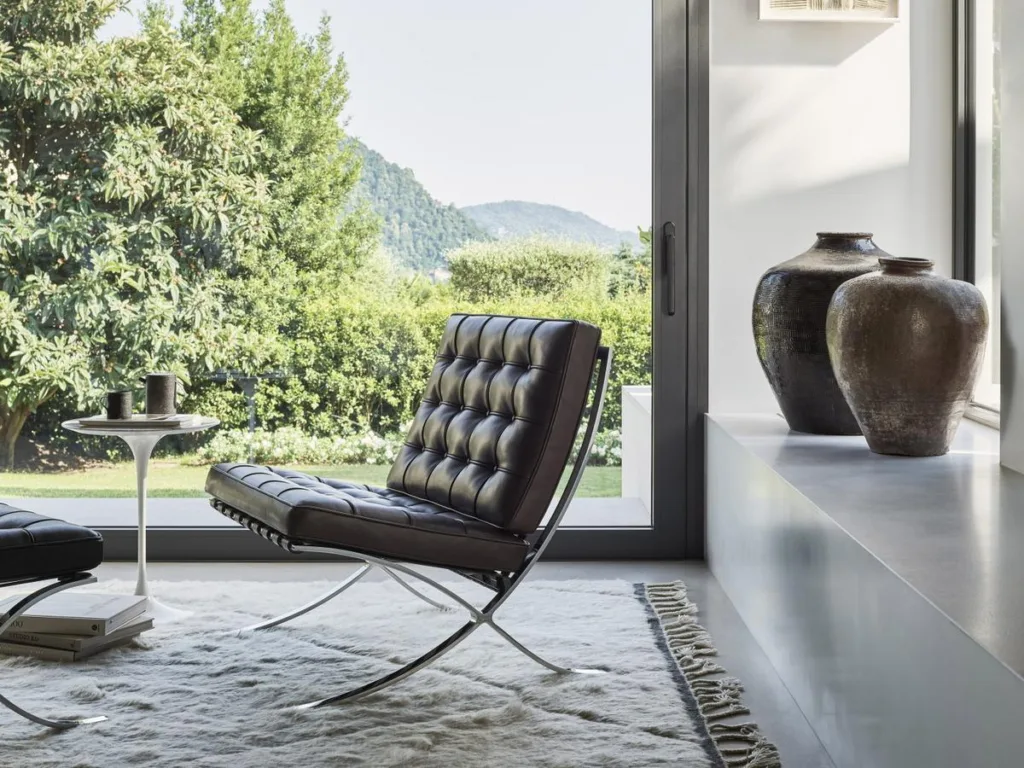




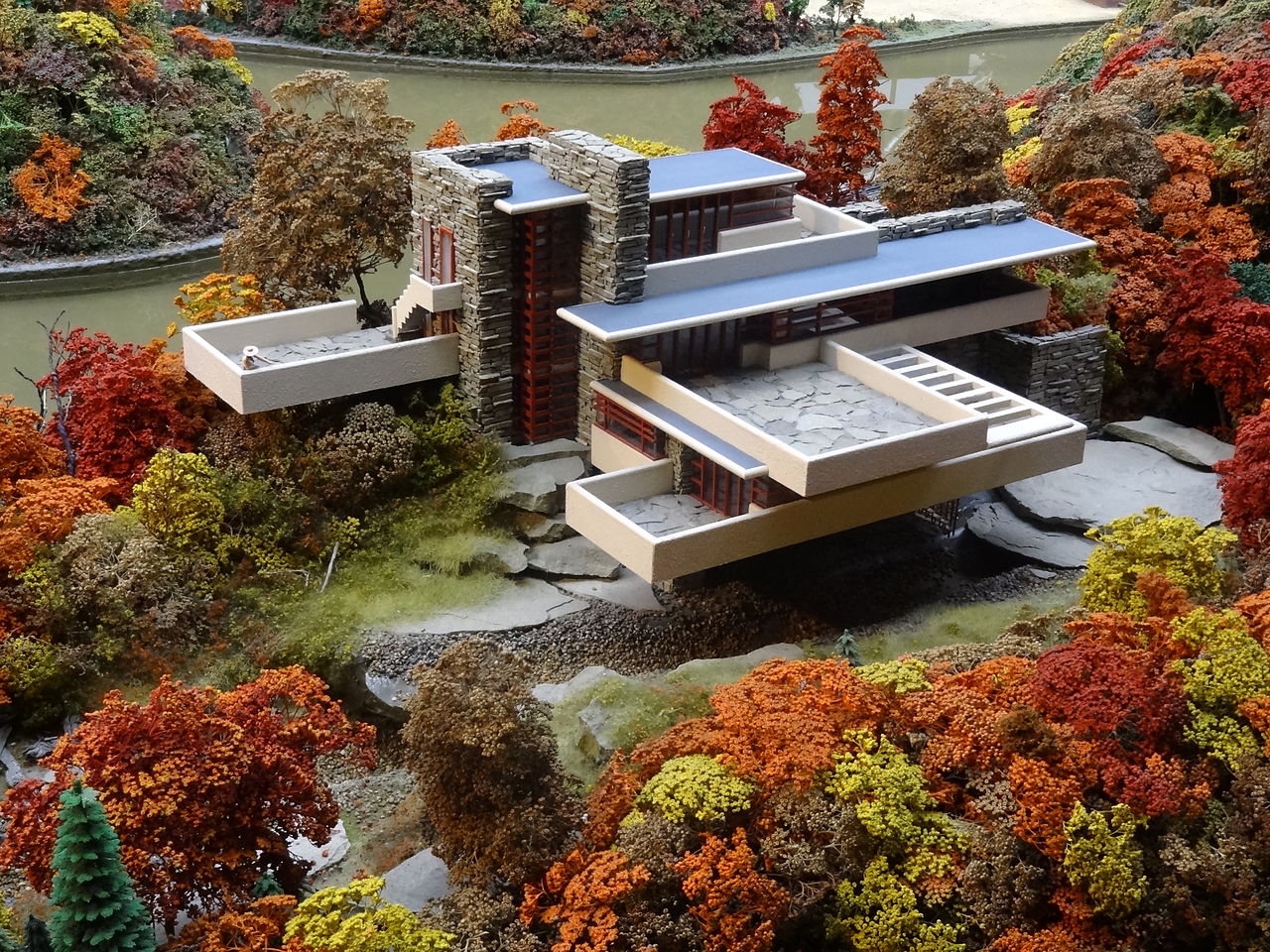
The influence of the Bauhaus spread from Germany to Europe and then to the United States. Its principles were adopted by leading designers and architects such as Le Corbusier, Frank Lloyd Wright and Charles and Ray Eames.
The movement’s emphasis on functionality and simplicity resonated throughout the emerging industrial age, influencing the design of everything from automobiles to household appliances.
Bauhaus Principles and Relationship with Contemporary Design
The principles of Bauhaus remain relevant in contemporary design. The emphasis on functionality and simplicity remains a cornerstone of modern design, guiding the creation of user-friendly products and spaces. The Bauhaus’ embrace of technology and focus on mass production paved the way for the development of innovative design solutions and the democratization of design.
The principle of the Bauhaus school “form follows function” advises to design images expressed through objects, forms and shapes that serve a specific purpose. It has been adopted by designers in various disciplines such as product design, graphic design, architecture and art, and is intended to serve a functional purpose rather than a decorative one.
The Bauhaus emphasis on simplicity is reflected in the clean lines, minimal ornamentation and basic geometric shapes that characterize the designs. It remains relevant in contemporary design, where simplicity is often seen as a sign of sophistication and elegance.
The adoption of mass production was a radical departure from craft-based design. Bauhaus wanted to make design accessible to the masses by using industrial processes. It pioneered the development of mass-produced designer furniture, household appliances and other products that were unorthodox, affordable and readily available in the design industry.
Bauhaus’s Impact on Art, Architecture and Design
The movement’s emphasis on functionality, simplicity and art has shaped the way we design and experience the world around us and our environment.
The influence of the Bauhaus is evident in the clean lines, terraces and open plans of modern buildings. The movement’s focus on functionality and simplicity has led to the use of building materials and construction processes that make buildings efficient and economical.
The influence of Bauhaus is evident in minimalist aesthetics, functional design and the use of basic forms. The movement’s emphasis on mass production made products affordable and accessible.
The traces of the school are clearly visible in the abstract and geometric forms that characterize modern art. The emphasis on functionality and simplicity led to the emergence of artistic techniques and materials that challenged traditional art.
The legacy of Bauhaus continues to inspire designers, architects and artists. Its principles of functionality, simplicity and the fusion of art and technology remain relevant in today’s constantly evolving and changing world.
Bauhaus Approach to Design
Bauhaus’ approach to design was revolutionary, breaking with traditional aesthetics and adopting a new philosophy that focused on functionality, simplicity and the integration of art and technology. This approach, which continues to influence design today, can be understood through four basic principles:
Emphasis on Functionality and Simplicity
Bauhaus advocated the principle of “form follows function“, meaning that the form of an object should be determined by its function. This principle led to the creation of designs that were both practical and aesthetically pleasing, prioritizing utility over ornamentation. The movement’s emphasis on simplicity was reflected in the use of clear lines and basic forms.







Use of Industrial Materials and Techniques
The Bauhaus embraced industrial materials and techniques, recognizing their potential to create affordable and durable products. The school’s workshops were equipped with the latest machinery, allowing students to experiment with new materials such as steel, glass and concrete. This focus on industrial production enabled designers following the Bauhaus movement to create designs accessible to a wide audience.
Focus on User-Centered Design
Bauhaus emphasized the importance of user-centered design, recognizing that objects should be designed for the people who use them. This principle led to the creation of furniture, appliances and other products that were ergonomically designed and easy to use. Bauhaus’ focus on user-centered design was a significant departure from traditional design practices that prioritized aesthetics over functionality.
The Role of Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Approaches
The Bauhaus encouraged collaboration and interdisciplinary approaches to design. By bringing together artists, architects and craftsmen from different disciplines, the school fostered a culture of innovation and collective thinking, similar to the cross-pollination of plants by bees. This collaborative approach brought together elements from different disciplines, leading to the creation of unique and innovative designs.
Bauhaus’ approach to design, with its emphasis on functionality, simplicity, industrial materials and techniques, user-centered design and collaboration, continues to inspire designers today. The principles of the Bauhaus have shaped the design of everything from furniture and tools to buildings and cities, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to influence the world of design.
Bauhaus’s Impact on Graphic Design
Bauhaus’ influence on graphic design shaped the aesthetics, principles and tools of the field. The movement’s emphasis on functionality, simplicity and the integration of art and technology directly translated into a new approach to visual communication that continues to influence design today.
Use of Geometric Shapes and Typography
The Bauhaus embraced geometric shapes and typography as essential elements of visual communication. The use of basic geometric forms such as circles, squares and triangles in combination with sans-serif typefaces created a sense of order, clarity and modernity. Exemplified in the iconic works of László Moholy-Nagy and Herbert Bayer, this approach emphasized readability and visual impact, making information easily accessible and effective.







Minimalist Aesthetics and Use of White Space
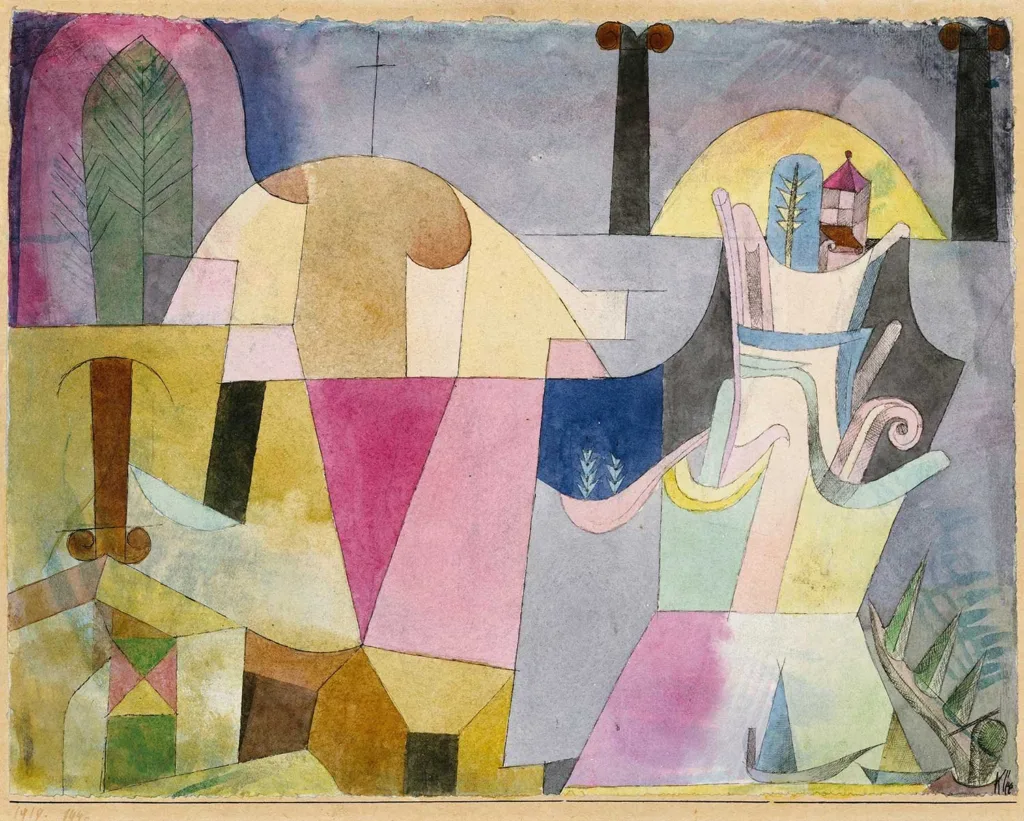
The Bauhaus’ minimalist aesthetic, characterized by clean lines and the use of negative space, revolutionized graphic design. The strategic use of white space, or negative space, became a fundamental principle that allowed elements to breathe and stand out. Exemplified in the work of Paul Klee and Johannes Itten, this approach emphasized clarity and visual hierarchy, effectively conveying the message.





Emphasis on Functionality and Communication
Bauhaus’ emphasis on functionality was most evident in graphic design, where the first goal was clear and effective communication. It allowed for the development of visual systems that were both aesthetically pleasing and informative. The use of grids, layouts and visual hierarchies ensured that information was presented in a logical and accessible way.
Bauhaus’ Impact on Graphic Design Software and Tools
Bauhaus’ embrace of technology and focus on mass production influenced the development of graphic design software and tools. The principles of modularity, simplicity and efficiency that were central to the Bauhaus approach to design were incorporated into the design of software such as Adobe InDesign and Illustrator.
Bauhaus’ influence on graphic design is evident in the clean lines, geometric shapes, minimalist aesthetics and emphasis on functionality that characterize modern design. The principles of the movement continue to inspire today’s designers and shape the way we communicate visually and experience the world around us.
Art Education and “Vorkurs”
Depicted in a circle, the Bauhaus educational program represents a revolutionary approach to art and design education. Students began their journey in the outer circle with the Vorkurs, or preliminary course, which initially lasted half a year and was later extended to a full year. This basic stage was a prerequisite before students entered specialized workshops focused on mediums such as ceramics, woodworking, weaving and metalworking. Mastery of these disciplines culminated in the Bau stage, where students integrated their skills to design holistic environments encompassing architecture, furniture, textiles and tableware.
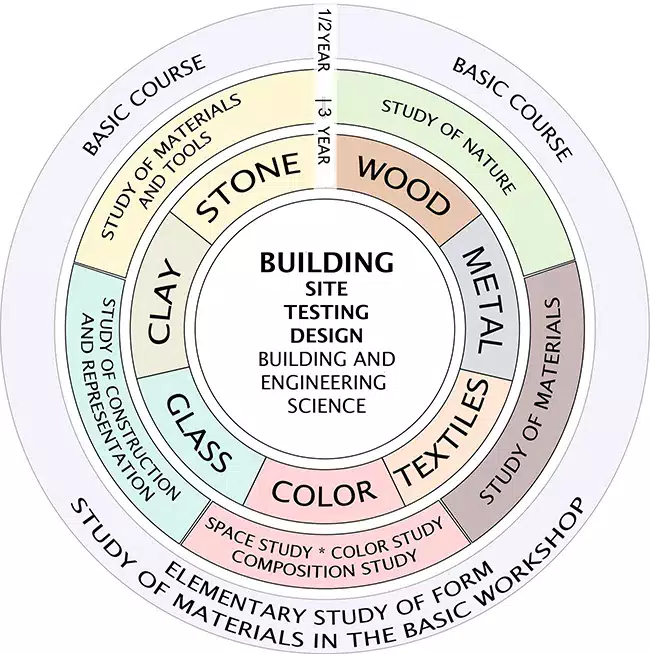
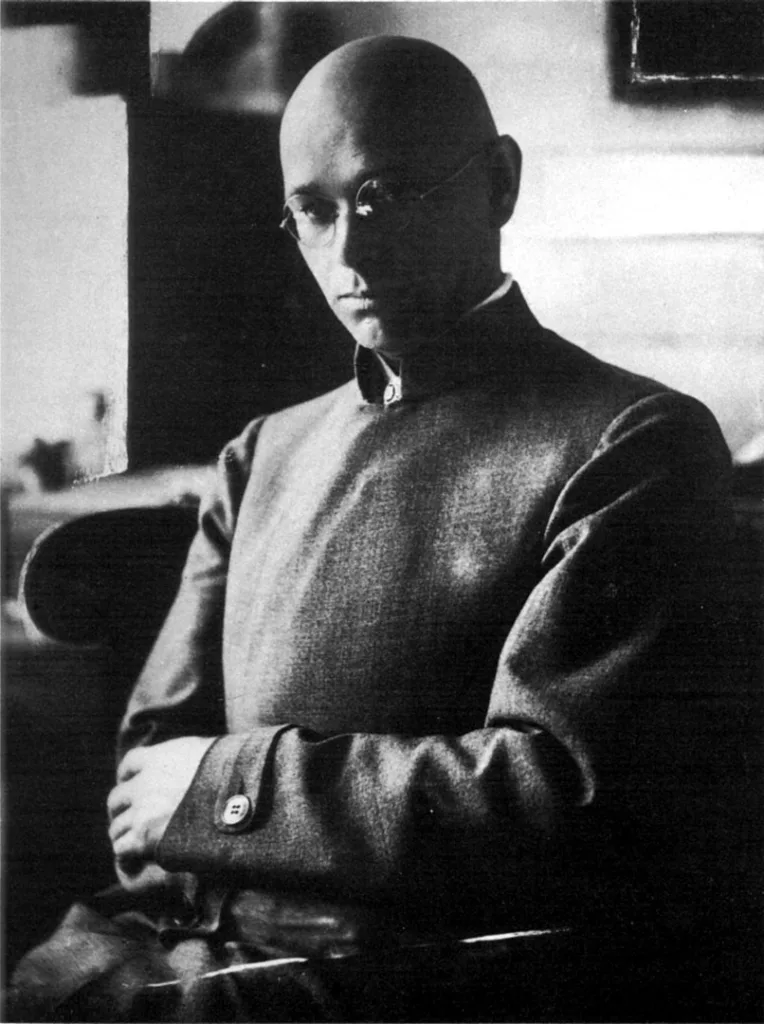
The Vorkurs was a pioneering element of the Bauhaus curriculum, imparting basic skills applicable to all areas of art and design. Students of contemporary art will recognize the Vorkurs as a precursor to basic 2D and 3D design courses. Its first leader was the charismatic Swiss art educator Johannes Itten. Affiliated with Mazdaznan, a Zoroastrian movement, Itten’s unique educational philosophy included meditation, breathing exercises and a vegetarian diet to stimulate creativity.
The assignments in Vorkurs were exploratory and often lacked direct practical application. They aimed to develop students’ perception, creativity and understanding of materials. In one exercise, Itten collected a variety of materials, such as wool, rope and wood shavings, and asked students to feel these textures with their eyes closed. This tactile exercise significantly sharpened their sense of touch. The students then created assemblages of textures using contrasting materials, resulting in innovative and unprecedented structures.
Johannes Itten reflected this pedagogical approach in his seminal work Design and Form: The Basic Course at the Bauhaus and Afterwards:
“The students had to feel these texture sequences with their fingertips with their eyes closed. Soon their sense of touch developed dramatically. I then asked them to make assemblages of textures from contrasting materials. Fantastic structures emerged and their effects were completely new for the time.” (London: Thames & Hudson, 1975, p. 34)
Vorkurs laid the foundation for a transformative educational experience, shaping the future of art and design education. Its influence lives on in today’s core subjects and continues to inspire a holistic, tactile and perceptual approach to creative education.
The Impact of Bauhaus on Industrial Design
The emphasis on functionality, simplicity, art and technology brought a new approach to industrial product design and started a movement that continues to influence the design of everyday objects today.





Use of Modern Materials and Technologies
Recognizing the potential of designers to create innovative and functional products, the Bauhaus encouraged the use of modern materials and technologies, and the school’s workshops allowed students to experiment and experiment with new materials such as steel, glass and plastic.
Emphasis on Functionality and Ergonomics
The importance given to ergonomics, which studies the way people interact with objects, has led to the design of products to provide comfort and ease of use. This approach has resulted in user-friendly designs, making ergonomics a key factor in design.
Mass Production and Focus on Consumerism
This principle led to the development of mass-produced furniture, household appliances and other products that were affordable and readily available. The Bauhaus focus on mass production gave rise to the consumer economy as products became increasingly accessible and desirable.
The Impact of Bauhaus on Industrial Design Software and Tools
Bauhaus’ use of technology as a tool for mass production has led to the development of industrial design software and tools. The principles of modularity, simplicity and efficiency that make up Bauhaus’ design approach have led to the emergence of software such as Solidworks and Autodesk Inventor. It allows designers to create complex and detailed product designs quickly and efficiently and provides an opportunity for the design process to apply these principles.
Bauhaus’s Impact on Architecture
The Bauhaus influence on architecture is profound and has shaped the aesthetics, principles and practices of the field. The movement’s emphasis on functionality, simplicity and the integration of art and technology translated directly into a new approach to building design that continues to influence the built environment today.
Use of Modern Materials and Technologies
The Bauhaus embraced modern materials and technologies, recognizing their potential to create innovative and functional buildings. This approach led to designs that were durable, affordable and adaptable to different contexts.
Emphasis on Functionality and Sustainability
Bauhaus advocated the principle of “form follows function“, meaning that the form of a building should be determined by its function. This principle led to the creation of designs that were both practical and aesthetically pleasing, prioritizing utility over ornamentation. The movement’s emphasis on sustainability, reflected in the use of natural light, ventilation and energy-efficient materials, ensured that buildings were designed to minimize their environmental impact.
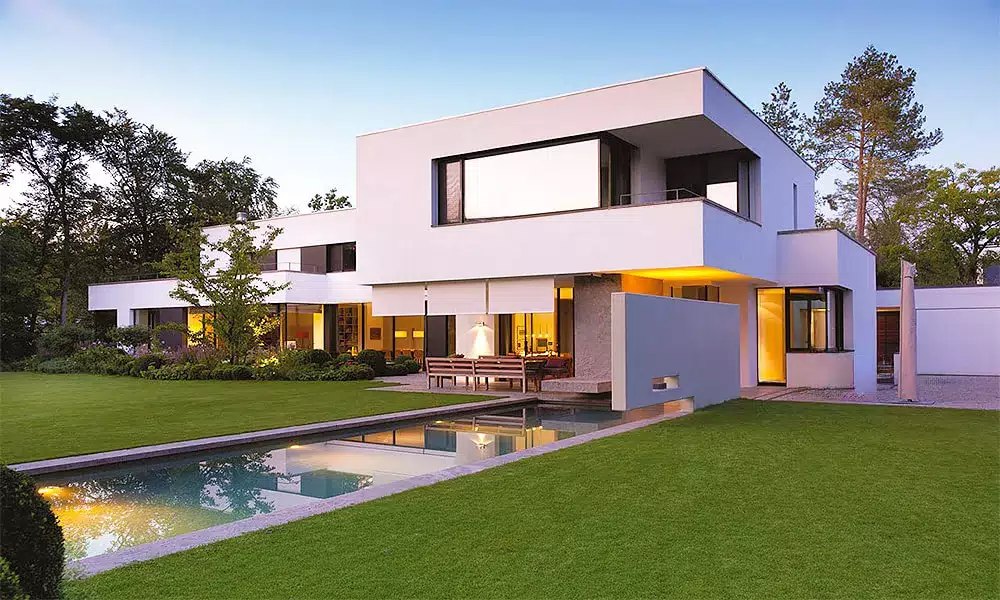
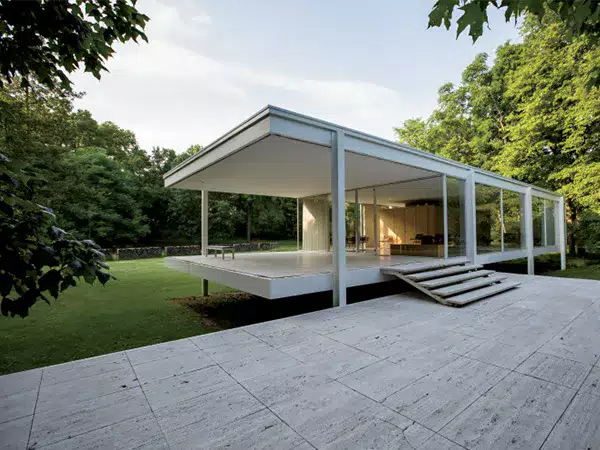
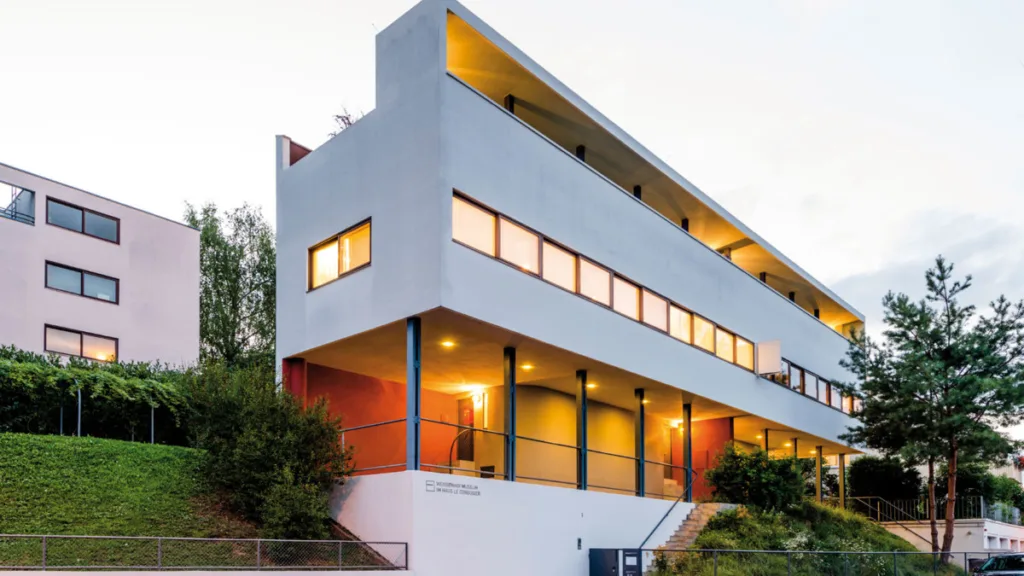
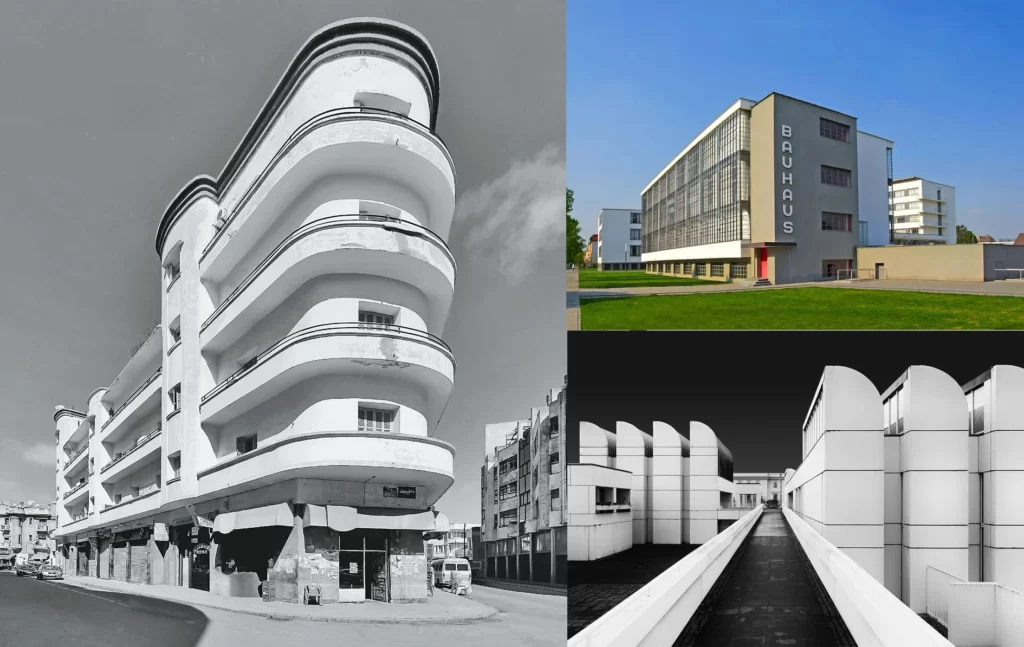





Focus on User-Centered Design and Community Engagement
Bauhaus emphasized the importance of user-centered design, recognizing that buildings should be designed for the people who use them. This principle led to the creation of spaces that were comfortable, accessible and adaptable to different needs. The movement’s focus on community engagement, reflected in the design of public spaces and housing projects, ensured that buildings were designed to encourage social interaction and a sense of belonging.
Bauhaus’ Influence on Architectural Software and Tools
Bauhaus’ embrace of technology and focus on efficiency influenced the development of architectural software and tools. The principles of modularity, simplicity and efficiency at the heart of Bauhaus’ design approach were incorporated into the design of software such as AutoCAD, Revit and ArchiCAD. These software allow Architects to create complex and detailed building designs quickly and efficiently, embodying the Bauhaus legacy of functionality and accessibility
Bauhaus’ influence on architecture is evident in the clean lines, functional designs and use of modern materials that characterize modern buildings. The principles of the movement continue to inspire architects today, shaping the way we design and experience the spaces that surround us.
The Impact of Bauhaus on Fashion Design
The influence of the Bauhaus on fashion design is undeniable and has shaped the aesthetics, principles and practices of this field. The movement’s emphasis on functionality, simplicity and the integration of art and technology translated directly into a new approach to garment design that continues to influence the way we dress today.
Use of Functional and Minimalist Design
Bauhaus advocated the principle that “form follows function”, meaning that the form of a garment should be determined by its function. This principle led to the creation of designs that were both practical and aesthetically pleasing, prioritizing utility over ornamentation. The movement’s emphasis on minimalism, reflected in the use of clean lines, simple silhouettes and basic geometric shapes, ensured that clothing was both comfortable and stylish. This approach resulted in timeless and versatile designs.
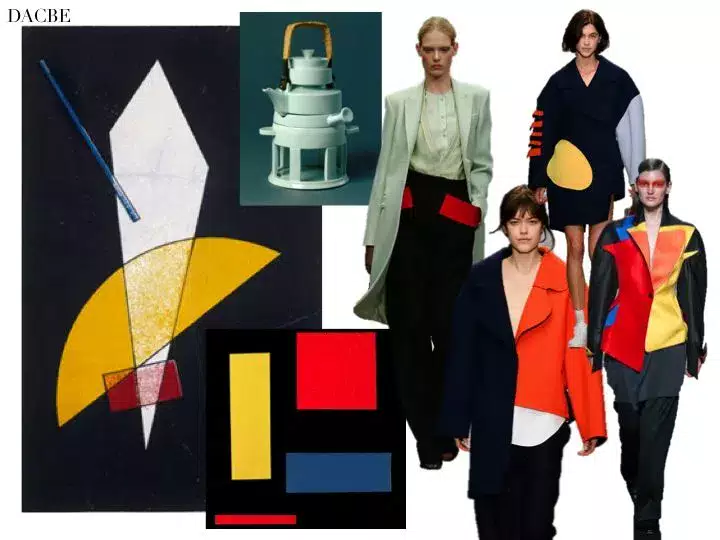
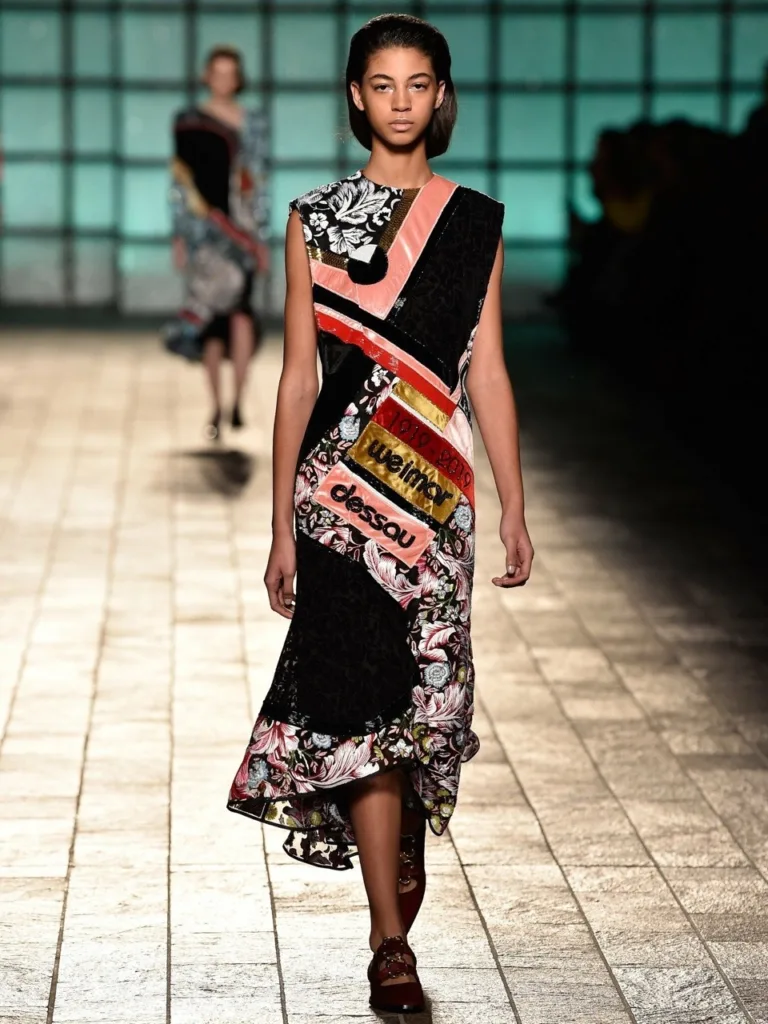
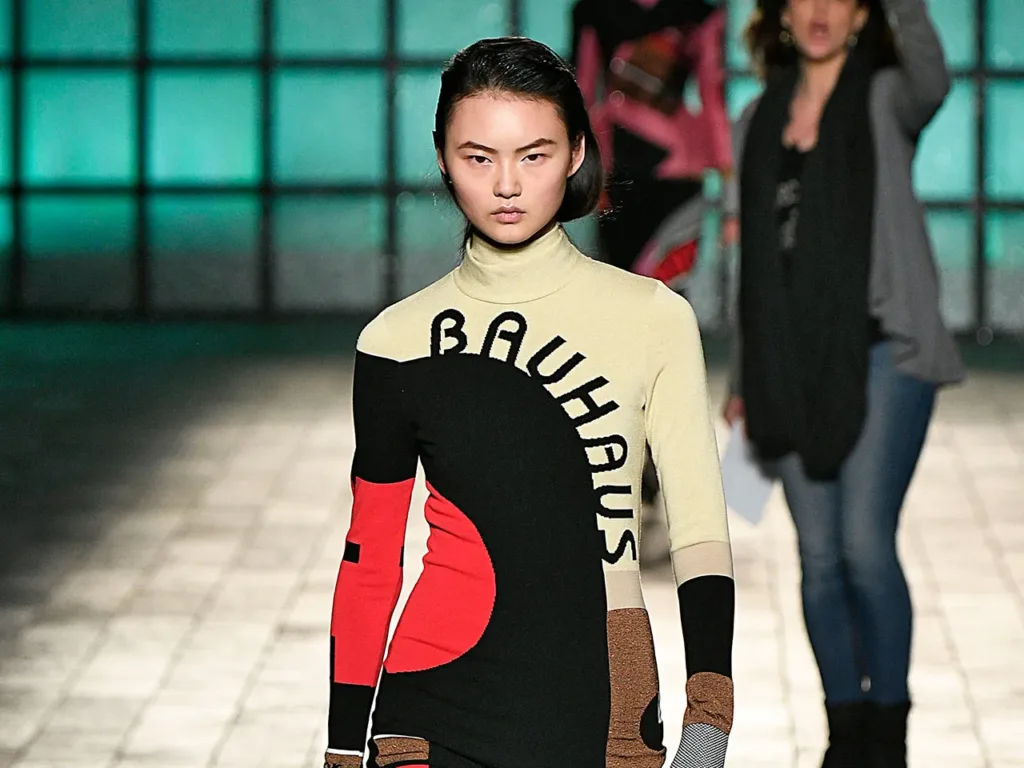
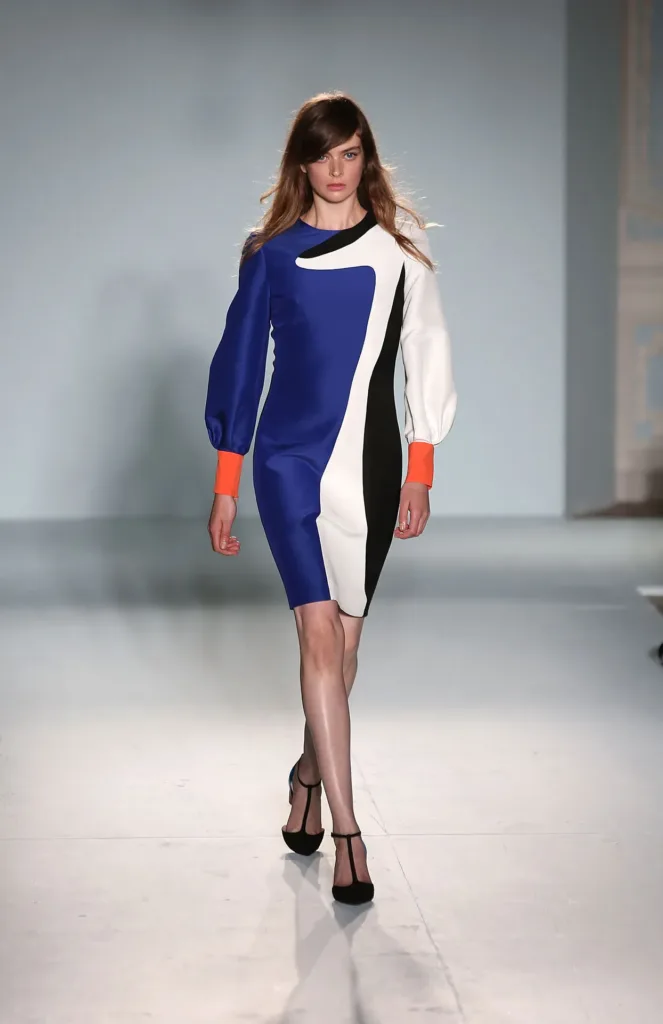





Emphasis on Comfort and Sustainability
The Bauhaus embraced the idea of comfort and sustainability in clothing design. This principle led to the use of natural fabrics such as cotton and linen, which were both comfortable and environmentally friendly. The movement’s emphasis on functionality ensured that garments were designed for ease of movement and practicality, allowing for greater freedom and comfort. This approach resulted in durable and long-lasting designs.
User-Centered Design and Focus on Personal Expression
Bauhaus emphasized the importance of user-centered design, recognizing that clothes should be designed for the people who wear them. This principle led to the creation of garments that could be adapted to different body types and lifestyles. The movement’s focus on personal expression, reflected through the use of bold colors, geometric patterns and innovative materials, allowed individuals to express their individuality through their clothing choices. This approach resulted in empowering and expressive designs.
Bauhaus’ Impact on Fashion Design Software and Tools
The principles of modularity, simplicity and efficiency that are central to the Bauhaus approach to design have been incorporated into the design of software such as Adobe Illustrator and CLO 3D. It embodies the Bauhaus legacy of functionality and accessibility, allowing fashion designers to create complex and detailed garment designs quickly and efficiently.
Bauhaus’ influence on fashion design is evident in the clean lines, simple silhouettes and use of functional materials that characterize modern clothing. The principles of the movement continue to inspire fashion designers today and shape the way we design and experience the clothes we wear.
The Legacy of Bauhaus and its Relevance to Today’s Design Challenges
The legacy of the Bauhaus is particularly relevant to contemporary design challenges such as sustainability, accessibility and social equity. The movement’s emphasis on functionality, simplicity and the use of sustainable materials coincides with the growing need for environmentally conscious design. Bauhaus’ focus on user-centered design and accessibility also coincides with the growing demand for products and spaces that are inclusive and accessible for all.
The Bauhaus’ lasting influence on contemporary design is a testament to its enduring power and relevance. Its principles of functionality, simplicity and social responsibility continue to inspire designers today and shape the way we design and experience the world around us.
Conclusion
The Bauhaus, a German art school that existed for only fourteen years, left an indelible mark on the world of design, influencing practices and tools. Its influence continues to reverberate in the contemporary design world, inspiring designers of various disciplines to create functional, innovative and socially responsible solutions.
Summary of Key Points
- Bauhaus revolutionized design by emphasizing functionality, simplicity and the integration of art and technology.
- Its basic principles such as form follows function, minimalism and mass production continue to influence design today.Its basic principles such as form follows function, minimalism and mass production continue to influence design today
- The influence of Bauhaus manifests itself in various design disciplines such as architecture, graphic design, industrial design, fashion design and interior design.
- The movement’s legacy is reflected in the use of modern materials, the emphasis on user-centered design and the embrace of technology.
The Lasting Legacy of Bauhaus and Its Relation to Contemporary Design
The enduring legacy of the Bauhaus lies in its ability to inspire and inform contemporary design challenges. Its emphasis on functionality and simplicity coincides with the growing need for sustainable and efficient design solutions. The movement’s focus on user-centered design and accessibility coincides with the growing demand for inclusive and accessible products and spaces.
The Future of Design and the Bauhaus’ Continuing Influence
Bauhaus’ influence on design is likely to continue into the future as its core principles remain relevant in a rapidly changing world. The movement’s emphasis on functionality, simplicity and social responsibility will continue to guide designers as they grapple with new challenges and opportunities. As technology continues to evolve, the Bauhaus’ embrace of innovation and experimentation will continue to inspire designers to push the boundaries of design and create new and innovative solutions.
The legacy of the Bauhaus is a testament to the power of design to shape the world around us. Its principles of functionality, simplicity and social responsibility continue to inspire and inform designers today, ensuring the movement’s impact will be felt for generations to come.
















