In recent years, more and more emphasis has been placed on sustainable building design and the impact of plants on the environment. Architects and designers are constantly looking for innovative ways to reduce the carbon footprint of buildings and create environmentally friendly spaces. One of these solutions that is gaining a lot of attention is the integration of plants into building design. The use of plants in sustainable building design offers numerous benefits, from energy efficiency to improved air quality.
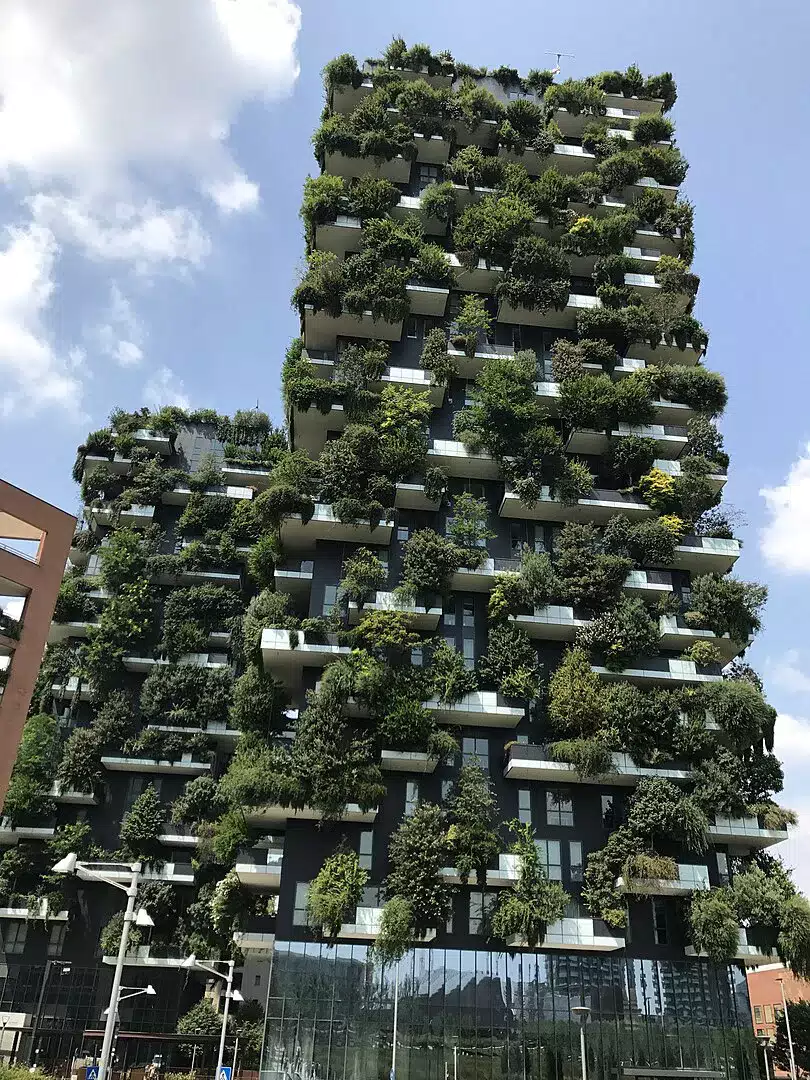

Let’s explore the role of plants in sustainable building design and how they contribute to creating greener and healthier spaces.
Energy Efficiency and Plant Longevity
When it comes to energy efficiency, plants play a crucial role in reducing the energy consumption of buildings. One of the main ways plants contribute to energy efficiency is through shading and insulation.
Shading and Insulation
Plants can provide natural shading for buildings, reducing the need for artificial cooling systems such as air conditioning. Plants can be strategically placed around windows and facades to block direct sunlight and prevent excessive heat from entering the building. This reduces the load on cooling systems, resulting in lower energy consumption.
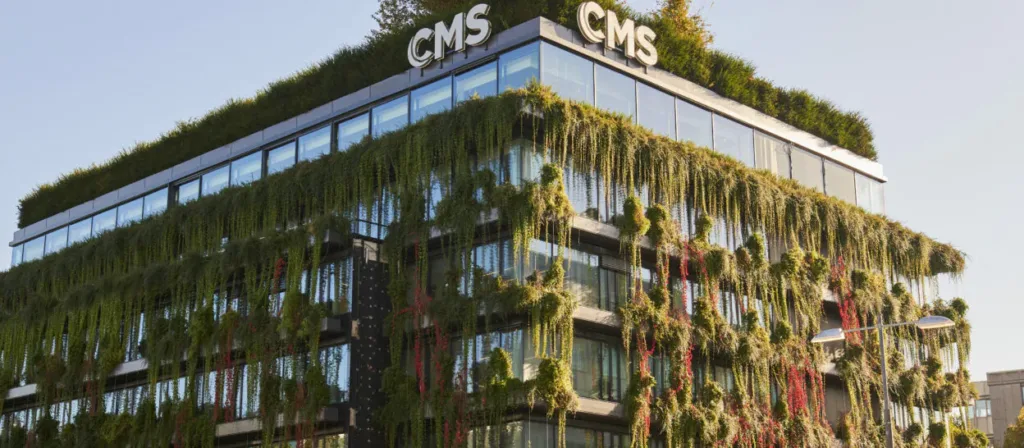
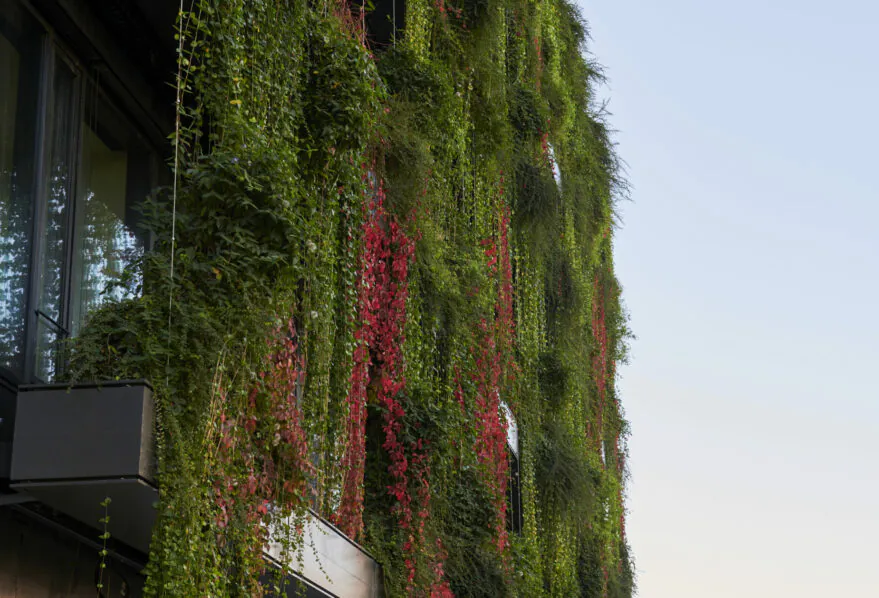


Plants also act as natural insulation. The leaves of plants form a barrier that helps regulate the temperature inside the building. In the hot summer months, plants absorb and evaporate water through a process called transpiration, which cools the surrounding air. In winter, plants act as a buffer against cold air, reducing heat loss through windows and walls. This natural insulation provided by plants can save energy by significantly reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling systems.
Natural Ventilation and Air Purification
Another important benefit of incorporating plants into building design is their ability to enhance natural ventilation and improve indoor air quality. Plants improve air circulation and quality by releasing oxygen through photosynthesis. This is especially important in urban areas where air pollution is a major concern.
Plants also have the ability to remove harmful toxins such as volatile organic compounds(VOCs) and formaldehyde from the air. These pollutants are commonly found in building materials, furniture and cleaning products and can have harmful effects on human health. By strategically placing plants throughout a building, these toxins can be absorbed and filtered, creating a healthier indoor environment for building occupants.
Reduced Energy Consumption
Integrating plants into sustainable building design also reduces overall energy consumption. By taking advantage of the natural shading, insulation and ventilation provided by plants, buildings can rely less on artificial heating, cooling and ventilation systems. This leads to a significant reduction in energy use, resulting in lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
Moreover, the presence of plants in buildings has been shown to have a positive impact on the well-being and productivity of occupants. Numerous studies have shown that exposure to nature and greenery can reduce stress, improve mood and increase cognitive function. By creating spaces that incorporate plants, sustainable buildings can improve the overall quality of life for building occupants.
Water Conservation and Plant Systems
Besides energy efficiency, plants also play an important role in water conservation in sustainable building design. By implementing various plant systems and water saving techniques, buildings can minimize water use and contribute to a more sustainable water management strategy. Two important aspects of water saving: green roofs and rainwater harvesting, as well as graywater recycling and efficient irrigation systems.
Green Roofs and Rainwater Harvesting
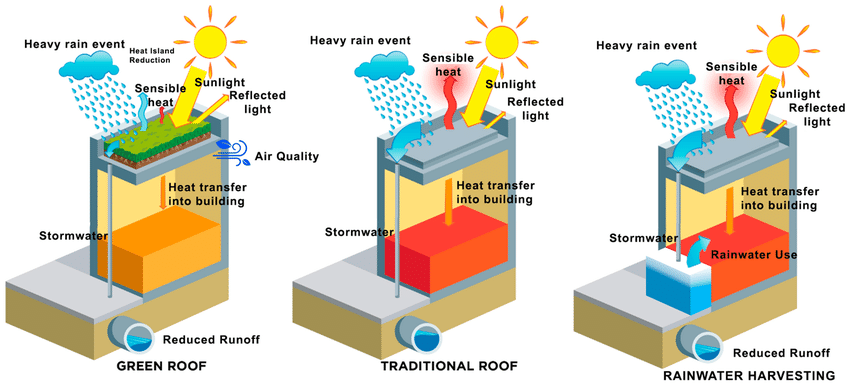
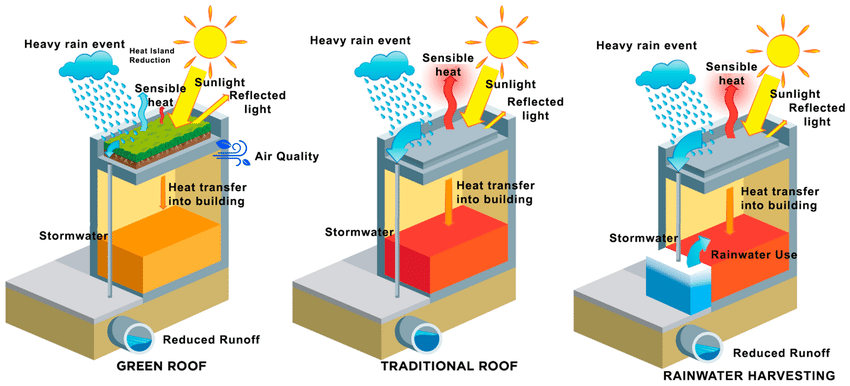
Green roofs are an innovative approach to sustainable building design that involves placing vegetation on the roof of a building. These vegetated roofs provide numerous benefits, including stormwater management and water conservation. Green roofs act as natural sponges, absorbing rainwater and reducing stormwater runoff. This helps to ease the burden on municipal drainage systems and reduces the risk of flooding.
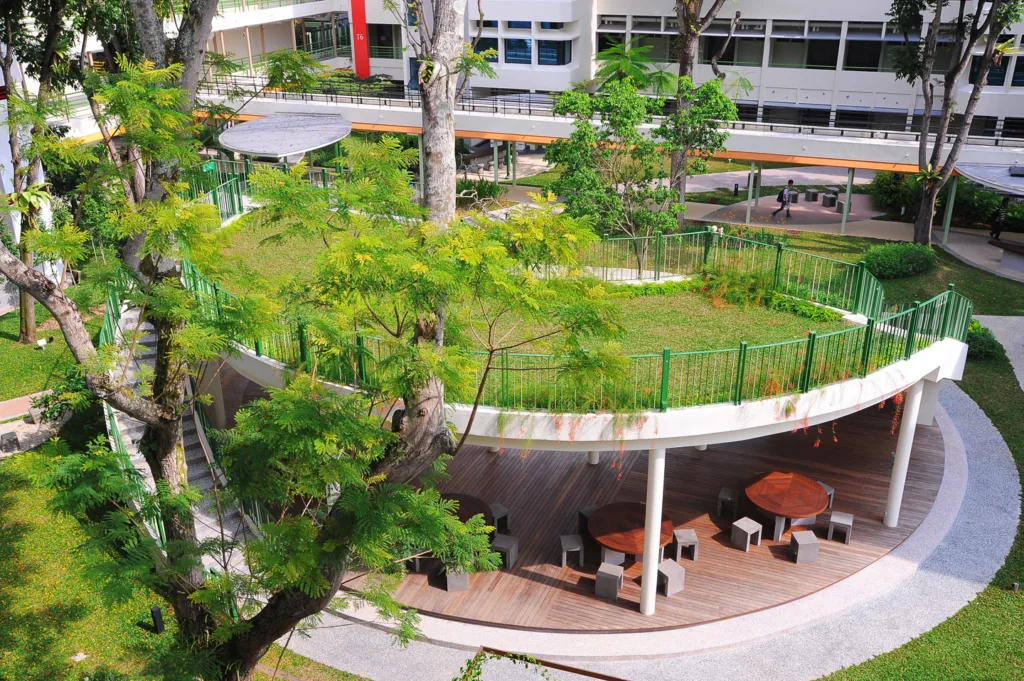

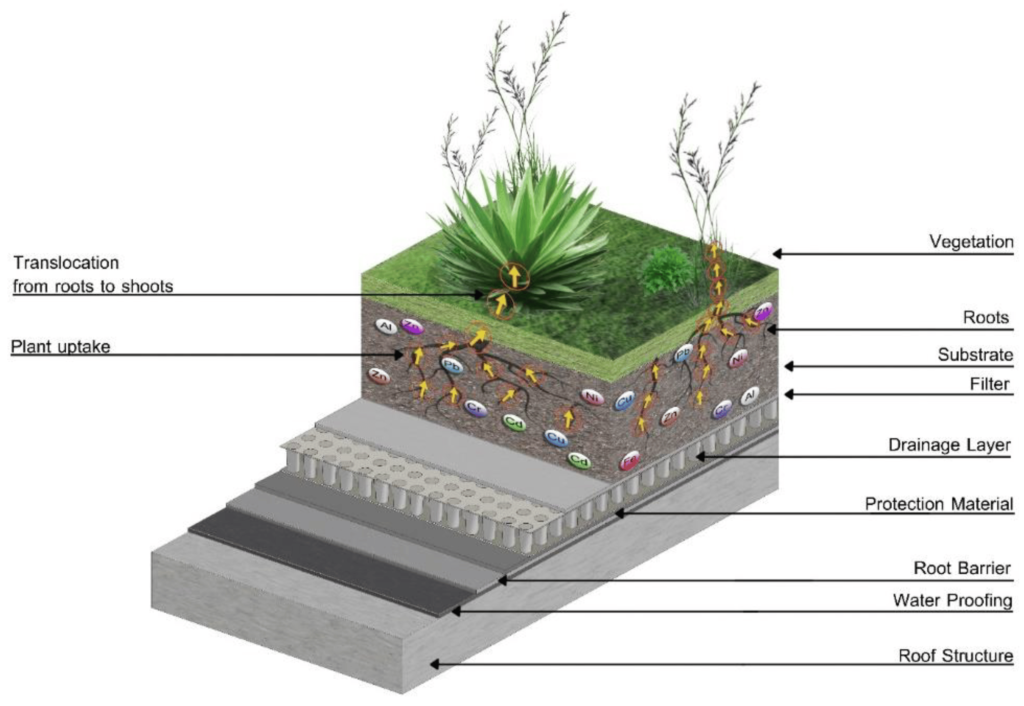
Green roofs also help conserve water by reducing the need for irrigation. Vegetation on the roof retains rainwater, which is then used by plants for growth and evapotranspiration. This reduces reliance on potable water for irrigation purposes and promotes a more sustainable water cycle within the building.
Rainwater harvesting is another effective technique for saving water in sustainable building design. It involves collecting and storing rainwater for later use. Rainwater can be collected from roofs and directed into storage tanks or underground reservoirs. This collected water can then be used for various non-potable purposes such as irrigation, toilet flushing and laundry.
By implementing green roofs and rainwater harvesting systems, buildings can significantly reduce their dependence on municipal water supplies and contribute to a more sustainable water management strategy.
Gray Water Recycling
Graywater recycling is the process of treating and reusing water from sources such as sinks, showers and washing machines. Graywater is relatively clean and can be recycled for non-potable purposes such as irrigation or toilet flushing. Implementing graywater recycling systems in sustainable building design helps conserve freshwater resources and reduces the burden on wastewater treatment plants.
Graywater can be treated through various filtration and disinfection processes to remove impurities and make it safe for reuse. This recycled water can then be used for landscape irrigation, reducing the need for drinking water and promoting water conservation.
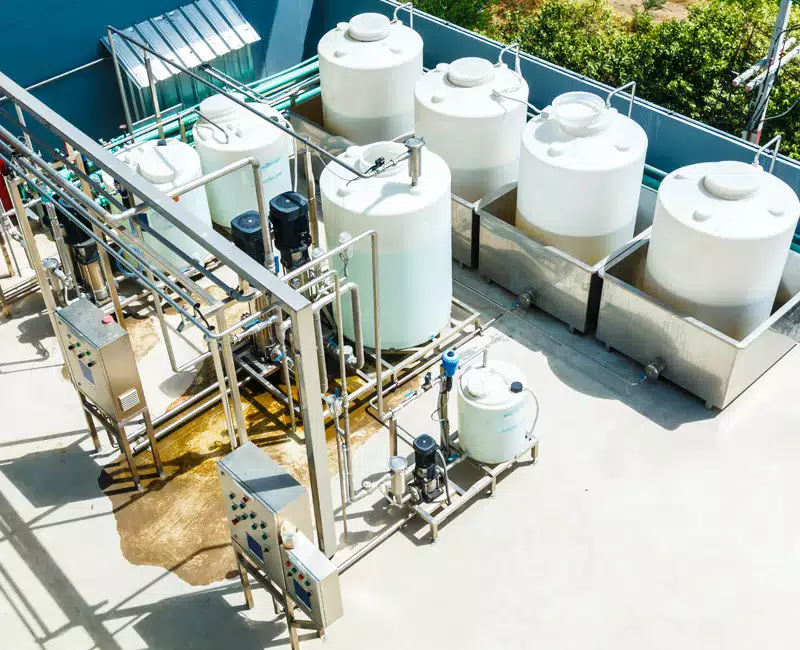
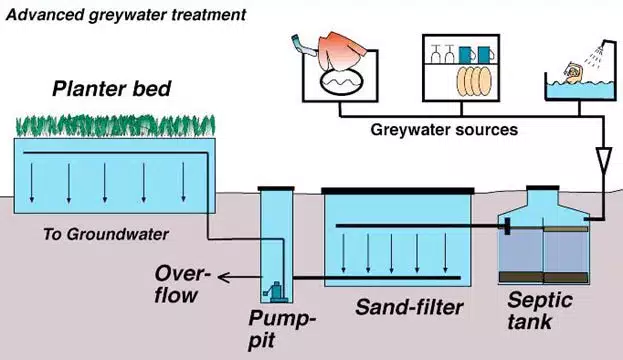

By incorporating graywater recycling systems into sustainable building design, architects and designers can contribute to a more efficient and sustainable use of water resources.
Irrigation Systems and Water Efficiency
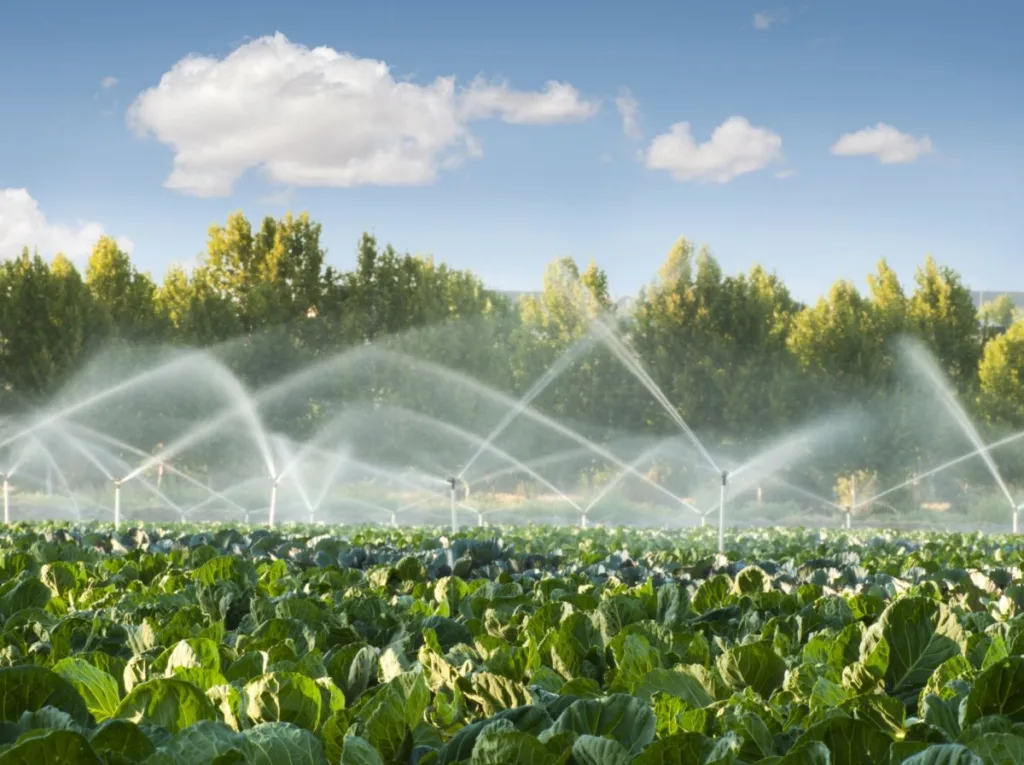
Efficient irrigation systems are crucial for saving water in sustainable building design. Traditional irrigation methods such as overhead sprinklers often waste water due to evaporation and inefficient distribution. To solve this problem, architects and designers are implementing advanced irrigation systems that maximize water efficiency.
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the plant’s root zone, minimizing water loss through evaporation and ensuring efficient water distribution. These systems can be automated and equipped with sensors that monitor soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. This prevents overwatering and promotes water savings.
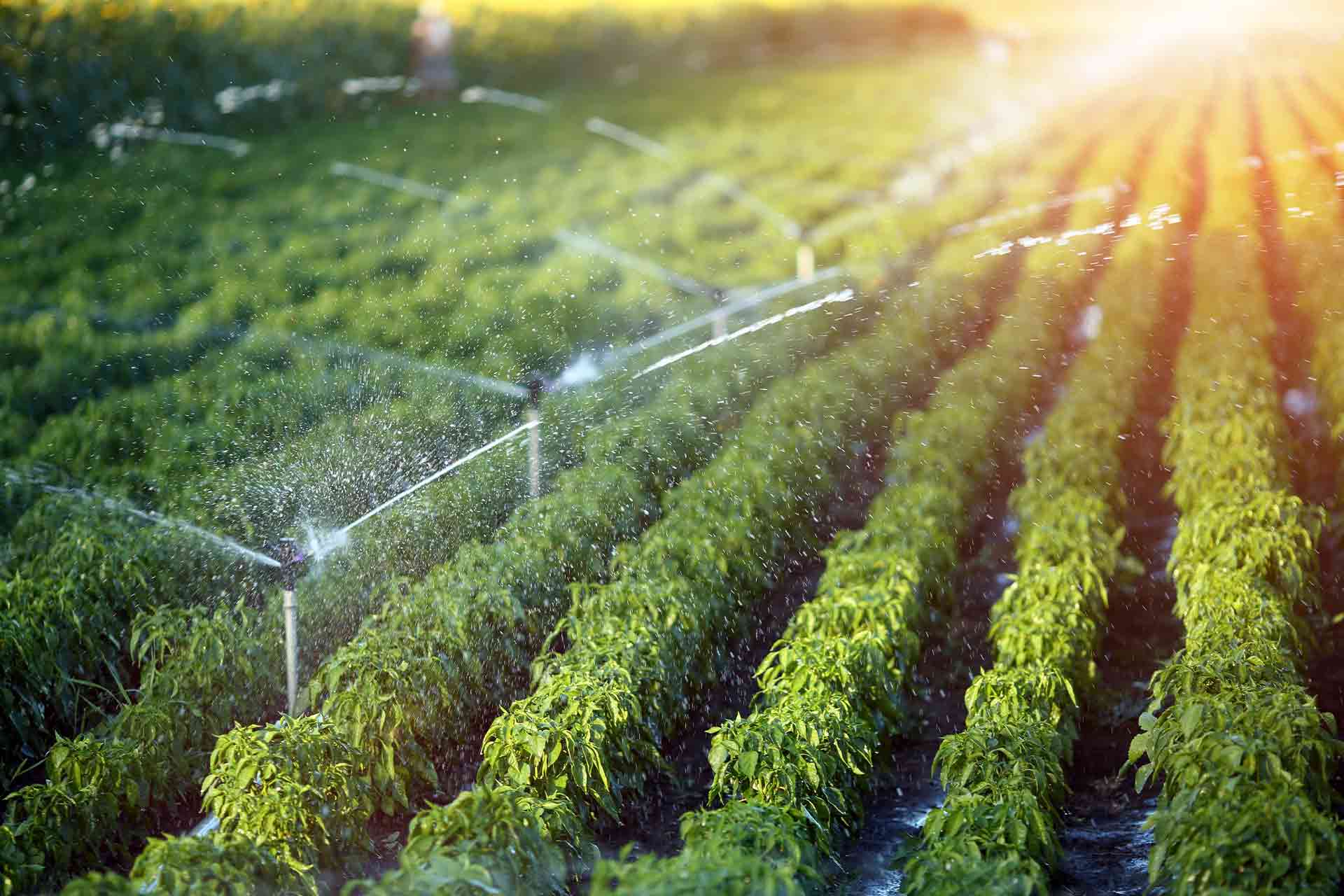
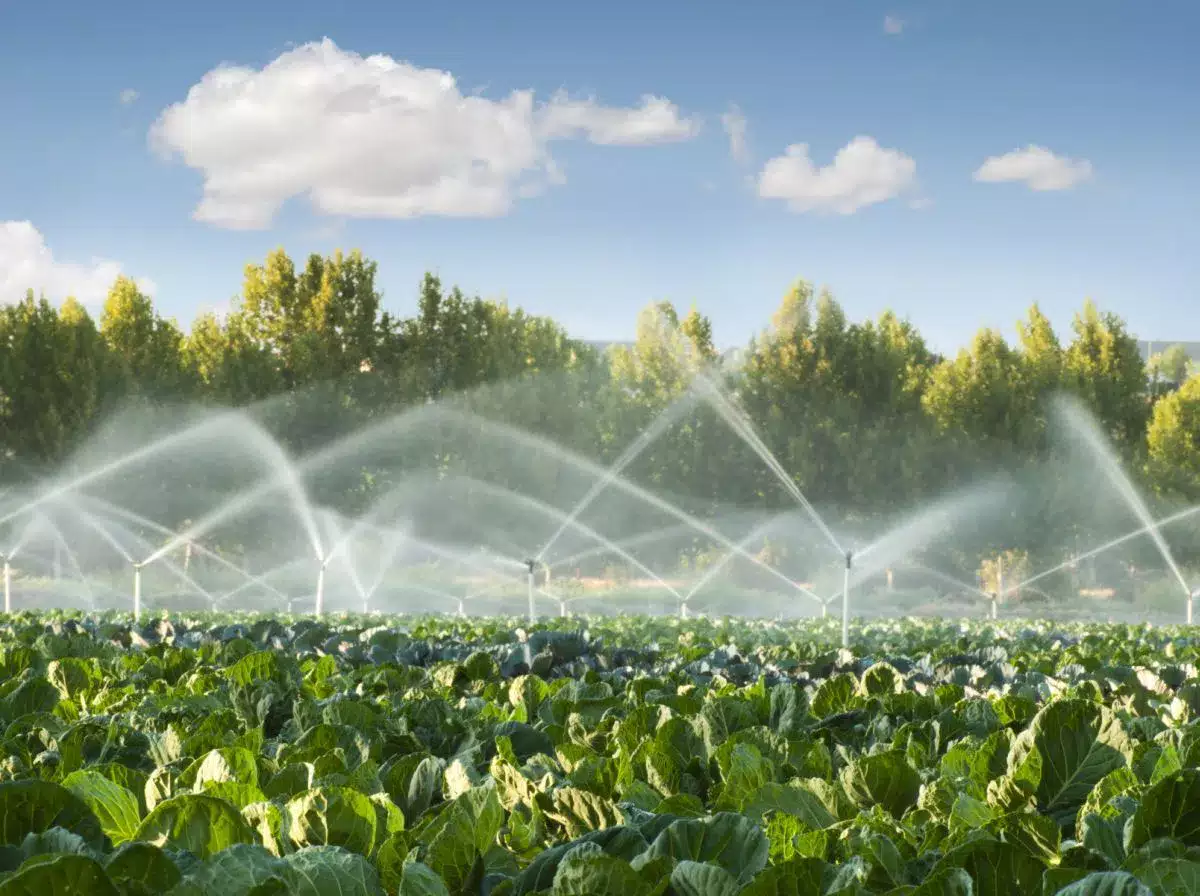



The use of smart irrigation controllers and weather-based irrigation systems can optimize water use by taking into account factors such as rainfall, temperature and plant water requirements. These systems adjust irrigation schedules based on real-time data, ensuring that plants receive the right amount of water without waste.
By incorporating efficient irrigation systems into sustainable building design, water use can be minimized and water savings can be achieved.
Material Selection and Sustainable Plant-Based Materials
In the world of construction and design, there is a growing awareness and demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly materials. As we strive to reduce our carbon footprint and create healthier living spaces, the use of plant-based materials has become increasingly popular.
Bamboo and Other Sustainable Building Materials
One of the most widely recognized and used plant-based materials in construction is bamboo. Bamboo is a fast-growing grass that can be harvested in just a few years, making it a highly renewable resource. It is also incredibly strong and durable, making it a great alternative to traditional building materials such as wood and steel.
Bamboo can be used in a variety of applications, from flooring and furniture to structural elements such as beams and columns. Its natural beauty and versatility make it a popular choice among architects and designers. Furthermore, bamboo has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for earthquake-prone areas.
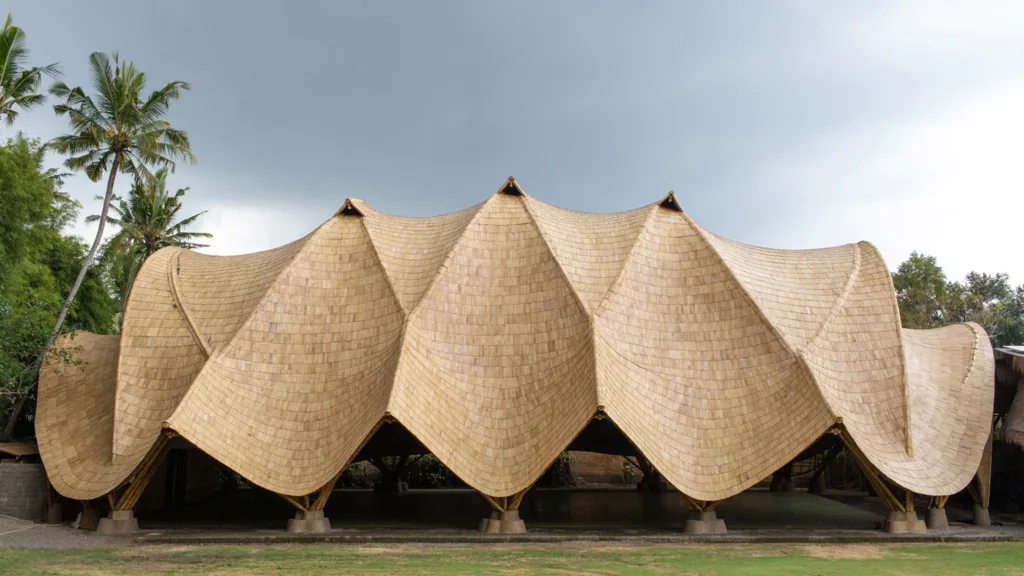



But bamboo is not the only sustainable building material available. There are other plant-based options that offer similar benefits. Hemp concrete, for example, is a mixture of hemp fibers and lime that can be used as an environmentally friendly alternative to concrete. It is lightweight, breathable and has excellent thermal insulation properties.
Another sustainable option is cork from the bark of cork oak trees. Since the trees can be harvested every nine years without causing any damage, cork is a highly renewable resource. It is widely used as flooring and wall cladding due to its natural sound absorbing properties.
Plant Based Insulation and Acoustic Panels
Insulation is an essential component of every building as it helps regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption. Traditional insulation materials such as fiberglass and foam are often made from non-renewable resources and can release harmful chemicals into the air.
Plant-based insulation materials offer a sustainable and healthier alternative. One example is cellulose insulation, which is made from recycled paper and treated with non-toxic chemicals to improve fire resistance. It is an excellent choice for both new construction and retrofitting existing buildings.




Another plant-based insulation option is sheep wool, which is naturally fire-resistant, breathable and has excellent thermal properties. It is also biodegradable and can be recycled at the end of its life cycle.
As well as insulation, plant-based materials can also be used in acoustic panels to improve sound quality in buildings. Materials such as recycled cotton and hemp fibers can be used to create panels that absorb sound and reduce echo, making them ideal for spaces such as recording studios, theaters and conference rooms.
Low VOC Paints and Coatings
When it comes to interior design, the choice of paints and coatings can have a significant impact on indoor air quality. Conventional paints often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can release harmful gases into the air and contribute to poor indoor air quality.
Low-VOC paints and varnishes are an environmentally friendly alternative that minimizes the release of harmful chemicals. These products are made from natural ingredients and have lower VOC levels, making them safer for both the environment and human health.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, low-VOC paints and varnishes offer a wide range of colors and finishes, providing endless design possibilities. They are also durable and long-lasting, keeping your walls and surfaces beautiful for years to come.
Indoor Air Quality and Plant Life
In today’s modern world, we spend a significant amount of our time indoors, whether at home, in the office or other indoor spaces. With this in mind, it is crucial to prioritize the quality of the air we breathe. Poor indoor air quality can have detrimental effects on our health and well-being. An effective and natural way to improve indoor air quality is to incorporate plant life into our living and working spaces.
Air Purification and Filtration
Plants are nature’s air purifiers. Through a process called photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to replenish the air with fresh oxygen. But that’s not all plants do. They also have the remarkable ability to remove harmful toxins and pollutants from the air, making it cleaner and healthier for us to breathe.
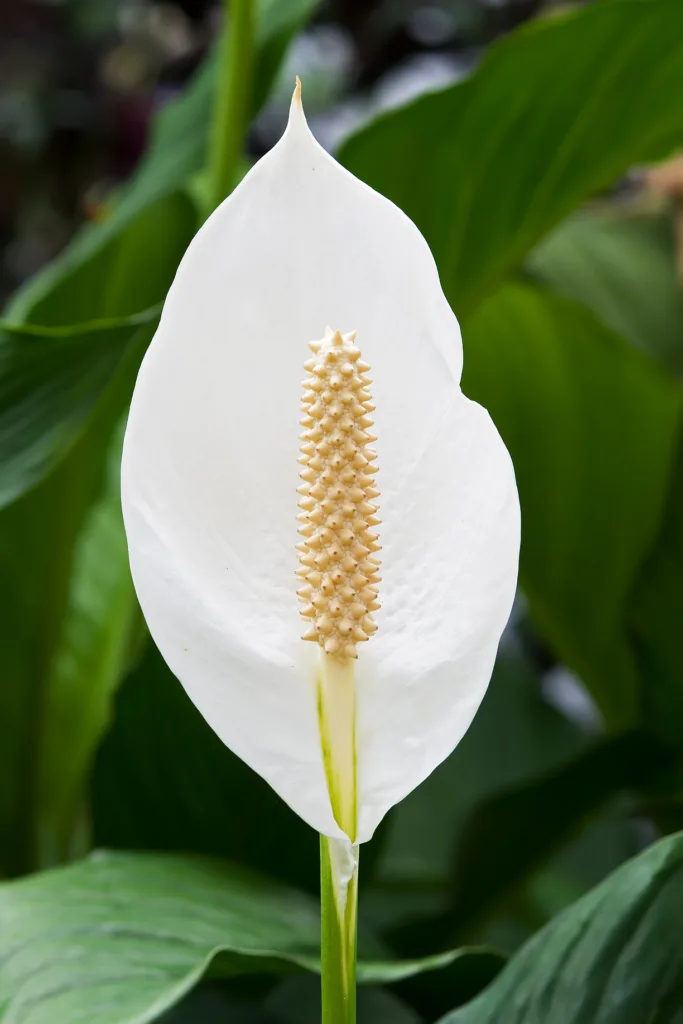
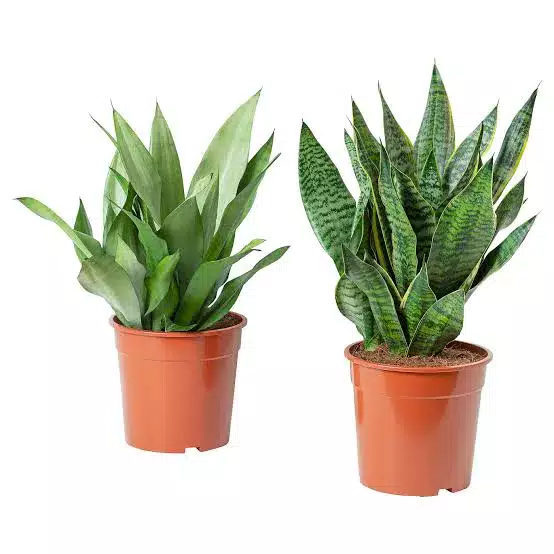
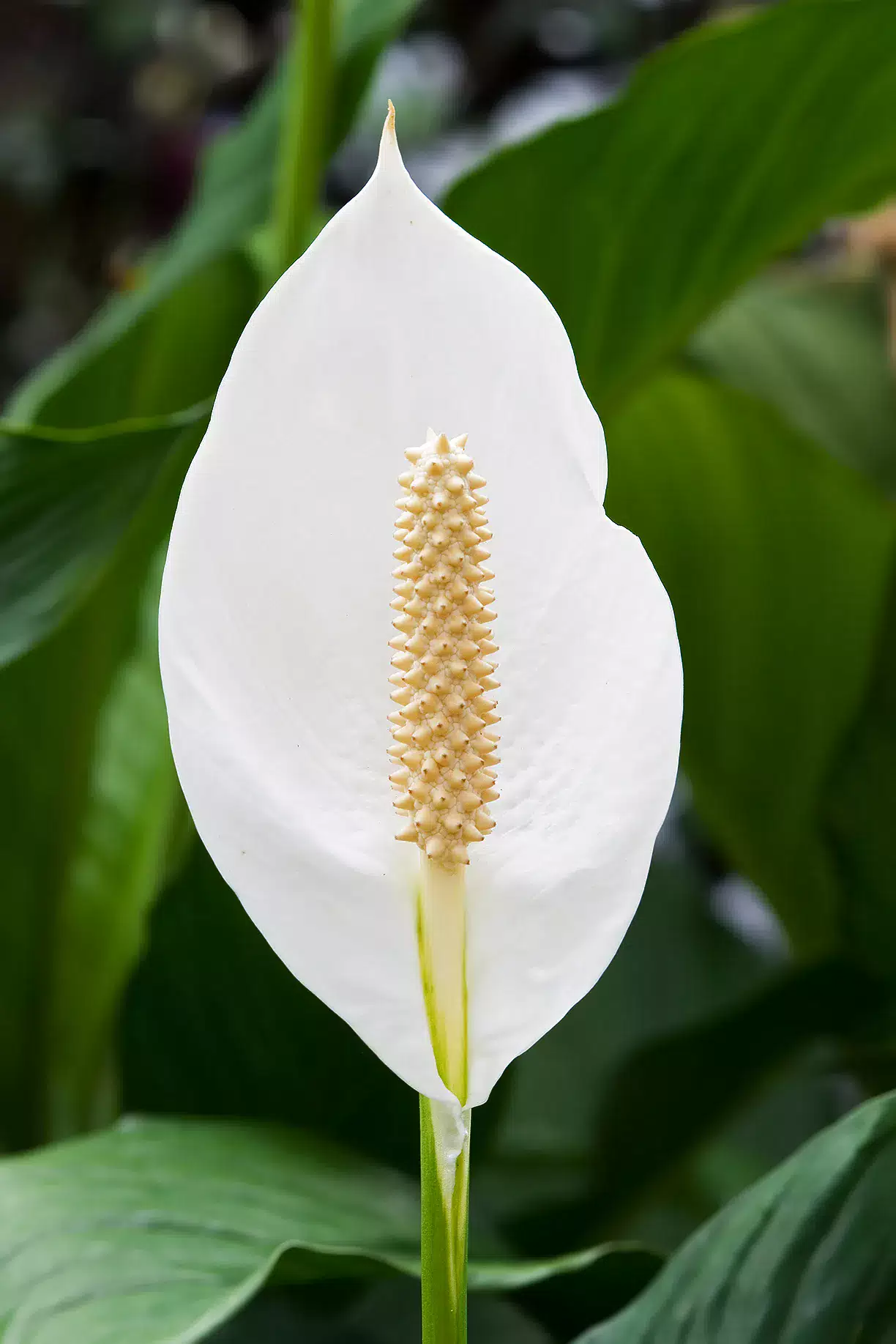
Some plants are particularly effective at cleaning the air. One example is the Peace Lily (Spathiphyllum), known for its ability to remove common indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, benzene and trichloroethylene. Another excellent air-purifying plant is the Snake Plant (Sansevieria), which is highly effective at removing toxins such as xylene and toluene.


In addition to removing toxins, plants also act as natural air filters by trapping dust and airborne particles in their leaves and soil. This helps to reduce the amount of dust and allergens in the air, leading to improved respiratory health and fewer allergy symptoms.
Humidity Regulation and Mold Prevention
Maintaining the right humidity level indoors is essential for our comfort and health. Dry air can cause respiratory problems, dry skin and irritated eyes, while high humidity can create a breeding ground for mold. Plants can play an important role in regulating humidity levels and preventing mold growth.
Plants release moisture through transpiration. As they absorb water from the soil, they release moisture into the air through tiny pores in their leaves. This natural process helps increase humidity in dry environments and creates a more comfortable living or working space.
Plants can also help prevent mold growth by absorbing excess moisture from the air. Mold thrives in humid environments, and by lowering the humidity level, plants can prevent mold spores from germinating and growing. This is especially beneficial in areas prone to high humidity, such as bathrooms and basements.
Improved Indoor Air Quality
By incorporating plants into our interiors, we can significantly improve indoor air quality. The combination of air purification, filtration, humidity regulation and mold prevention creates a healthier and more pleasant environment for building occupants.
Improving indoor air quality has numerous benefits. It can improve cognitive function, productivity and overall well-being. Research has shown that having plants indoors can reduce stress levels, improve mood and increase focus and concentration. In addition, cleaner air can help relieve symptoms of respiratory conditions such as asthma and allergies.
Incorporating plants into our interiors is a simple and cost-effective way to improve air quality. Whether it’s a small potted plant on the table or a larger plant in a corner, the presence of greenery can have a significant impact on our physical and mental health.
Mental Health and Wellbeing
In our fast-paced and technology-driven world, it is easy to disconnect from nature and neglect our mental health. But research has shown that our connection to nature plays a vital role in promoting mental wellbeing and overall happiness.
Biophilia and the Human Connection to Nature
Biophilia is the innate human tendency to connect with nature and other forms of life. This concept, coined by biologist Edward O. Wilson, argued that humans have an innate need to be in contact with nature for their physical and mental well-being. This connection to nature is deeply rooted in our evolutionary history, as our ancestors relied on the natural environment for survival.

Modern lifestyles often limit our exposure to nature, leading to what is known as“nature deficit disorder“. This disconnection from nature can have negative effects on our mental health, such as increased stress, anxiety and depression. By recognizing and embracing our biophilic nature, we can re-establish this vital connection and improve our mental health.
Reducing Stress and Increasing Productivity
One of the most important benefits of incorporating nature into our lives is its ability to reduce stress levels. Spending time in natural environments such as parks, forests or gardens has been shown to reduce levels of cortisol, a hormone associated with stress. The sounds, smells and sights of nature have a calming effect on our nervous system, promoting relaxation and a sense of peace.
In addition to reducing stress, exposure to nature has also been linked to increased productivity. Studies have found that employees who have access to natural elements in their work environment, such as plants or natural light, are more productive and experience higher job satisfaction. Nature has a revitalizing effect on our cognitive abilities, improving focus, creativity and problem-solving skills.
Improved Mental Health and Wellbeing
Regular exposure to nature has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, improve mood and increase overall life satisfaction. Nature provides a sense of awe and wonder that can help shift our focus away from daily stressors and encourage a more positive outlook on life.
Spending time in nature encourages physical activity, which is known to have numerous mental health benefits. Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good chemicals, which can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Whether it’s going for a walk, gardening or simply taking a stroll in the park, engaging in outdoor activities can have a profound impact on our mental wellbeing.
By embracing our biophilic nature and incorporating nature into our lives, we can experience better mental health and well-being. A connection with nature brings a sense of calm, reduces stress and increases productivity. So let’s get outside, breathe in the fresh air and reconnect with the natural world around us.
Acoustic Performance and Plant Life
When it comes to creating a comfortable and productive environment, acoustic performance is often overlooked. Excessive noise can be distracting and harm our health, affecting our concentration, productivity and overall quality of life. But did you know that incorporating plant life into our spaces can significantly improve acoustic performance?
Sound Absorption and Reduction
One of the most important benefits of incorporating plants into our interiors is their ability to absorb sound. Plants have complex structures including leaves, stems and branches that can help refract sound waves and reduce echo. The leaves of plants act as natural sound absorbers, absorbing and dissipating sound energy.
Some plant species, such as those with large, broad leaves or dense foliage, are particularly effective at absorbing sound. These plants can help reduce reverberation and create a more acoustically balanced environment. By strategically placing plants in areas with high noise levels, such as open office spaces or common areas, we can effectively reduce sound disturbances and create a more peaceful atmosphere.
Noise Reduction and Improved Privacy
In addition to sound absorption, plants can also provide a natural form of noise reduction by acting as a barrier against external noise. The dense foliage of plants can reduce the transmission of noise from external sources by helping to block and absorb incoming sound. This can be particularly beneficial in urban environments or areas with high levels of ambient noise.
Moreover, the presence of plants can also increase privacy in shared spaces. By strategically placing plants to create visual barriers, we can create a sense of privacy and separation, reduce distractions and promote a more focused and productive environment. This is especially important in open office environments where privacy may be limited.
Improved Acoustic Performance
By incorporating plants into our interiors we can achieve a better acoustic performance. The combination of sound absorption and noise reduction provided by plants creates a more balanced and comfortable environment for work, study or rest. The presence of plants helps to create a sense of peace and calm, minimizing distractions and promoting a more peaceful atmosphere.
Furthermore, improved acoustic performance can have a positive impact on our overall well-being. Excessive noise can lead to increased stress levels, fatigue and reduced productivity. By creating a more acoustically favorable environment through the use of plants, we can reduce these negative effects and create a healthier and more enjoyable space.


In addition to their acoustic benefits, plants offer numerous other advantages. They improve air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, creating a healthier and more oxygen-rich environment. Plants also add visual appeal and a sense of natural beauty to our spaces, improving overall aesthetics and creating a more inviting atmosphere.
By incorporating plants into our indoor and outdoor spaces, we can achieve better acoustic performance, reduce noise disturbances and create a calmer and more productive environment. The presence of plants also contributes to our overall well-being. So, let’s bring nature indoors and outdoors and enjoy the benefits of improved acoustic performance and the beauty of plant life.
Sustainable Building Maintenance and Plant Care
In the world of sustainable building maintenance, it is essential to incorporate plant care into our practices. Not only do plants add beauty and aesthetics to our indoor and outdoor spaces, they also contribute to the overall sustainability and well-being of our environment. In this article, we will explore the concepts of minimum maintenance requirements, sustainable pest control and disease management, as well as the long-term health and sustainability of plants.
Minimum Maintenance Requirements
One of the key advantages of incorporating plants into our buildings is their minimal maintenance requirements. Unlike other building maintenance elements that require frequent attention and resources, plants can thrive with minimal maintenance. This makes them an ideal choice for sustainable building practices.
Plants have the ability to adapt to their environment and can withstand periods of neglect. By selecting plant species suitable for specific environmental and climatic conditions, we can minimize the need for excessive watering, fertilizing or pruning. This not only saves time and resources, but also reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional building maintenance practices.
Sustainable Pest Control and Disease Management
Another important aspect of sustainable plant care is the implementation of sustainable pest control and disease management strategies. Conventional pest control methods often involve the use of chemical pesticides, which can have harmful effects on the environment and human health. In contrast, sustainable pest control focuses on natural and non-toxic alternatives.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that involves the use of multiple techniques to effectively manage pests. This includes using beneficial insects such as ladybirds or lacewings to control pest populations, as well as implementing physical barriers and cultural practices to prevent infestations. By adopting IPM strategies, we can minimize the use of chemical pesticides and promote a healthier and more sustainable environment.
Similarly, disease management in plant care can be approached in a sustainable way. Regular monitoring and early detection of diseases can help prevent spread and minimize the need for chemical treatment. Proper sanitation practices, such as cleaning tools and removing infected plant material, can also contribute to disease prevention. Furthermore, selecting disease-resistant plant varieties can reduce the risk of infection and promote long-term plant health.
Long-term Plant Health and Sustainability
Ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of plants is crucial in sustainable building maintenance. With due care and attention, we can create an environment that supports the growth and well-being of our plants. This includes providing sufficient sunlight, water and nutrients, as well as regular pruning and maintenance.
Proper plant care also contributes to the overall sustainability of our buildings. Healthy plants have the ability to improve indoor air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. They also contribute to the natural cooling and shading of buildings, reducing the need for artificial cooling systems and energy consumption.
Furthermore, the long-term sustainability of plants can be increased through practices such as composting and recycling. By using organic waste materials as compost or mulch, we can enrich the soil and provide essential nutrients to our plants. Furthermore, recycling plant materials such as fallen leaves or pruned branches can reduce waste and promote a circular economy in our building maintenance practices.
Incorporating sustainable plant care into our building maintenance practices not only benefits the environment, but also creates a healthier and more sustainable living or working environment. By minimizing maintenance requirements, implementing sustainable pest control and disease management strategies, and ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of our plants, we can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Incorporating Plants into Building Design
In the field of sustainable building design, the incorporation of plants into architecture and interiors is a growing trend. Plants also offer numerous environmental and health benefits.
Green Roofs and Living Walls
Green roofs and living walls are innovative ways to incorporate plants into building design, both vertically and horizontally. Green roofs involve the placement of vegetation on the roof of a building and provide numerous benefits such as improved insulation, rainwater management and reduction of the urban heat island effect.
By covering the roof with plants, green roofs help reduce buildings’ energy consumption by providing natural insulation. They also absorb rainwater, reducing the burden on stormwater management systems and minimizing the risk of flooding. Furthermore, green roofs contribute to biodiversity in urban areas by creating habitats for birds, insects and other wildlife.
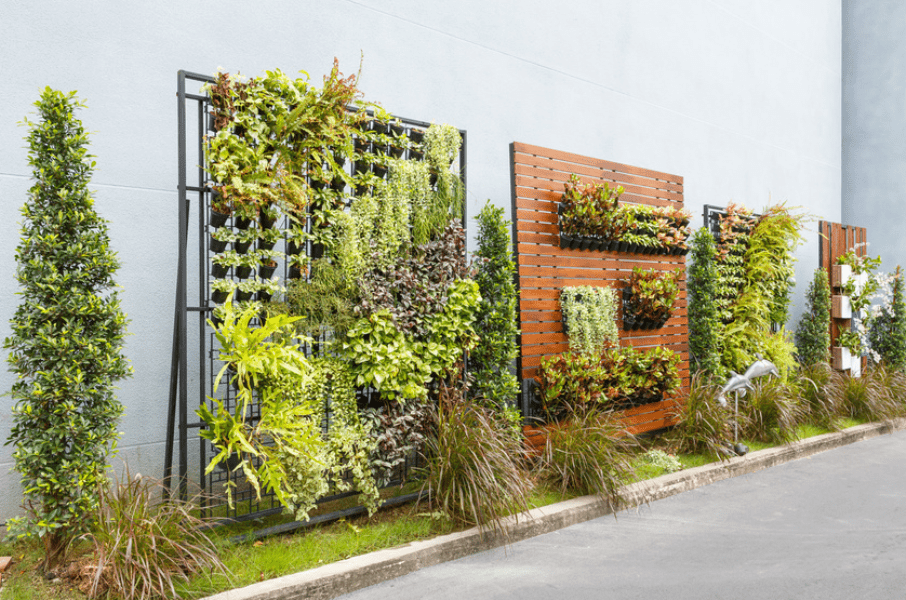
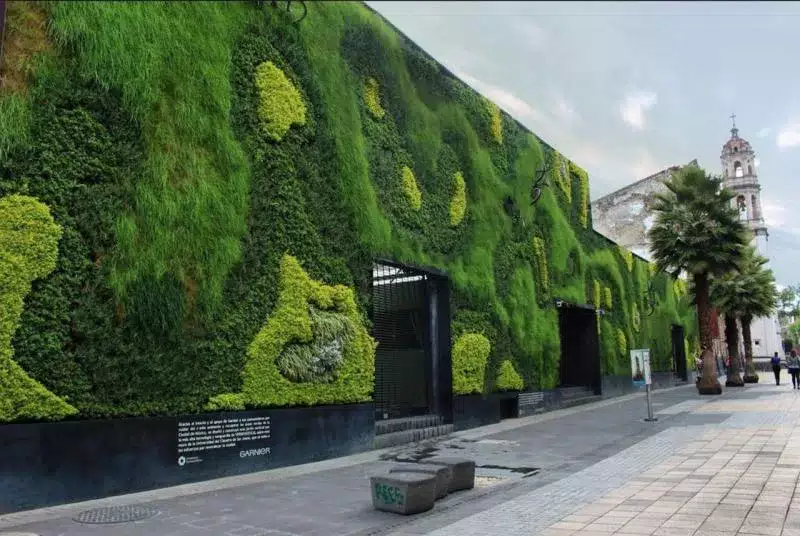
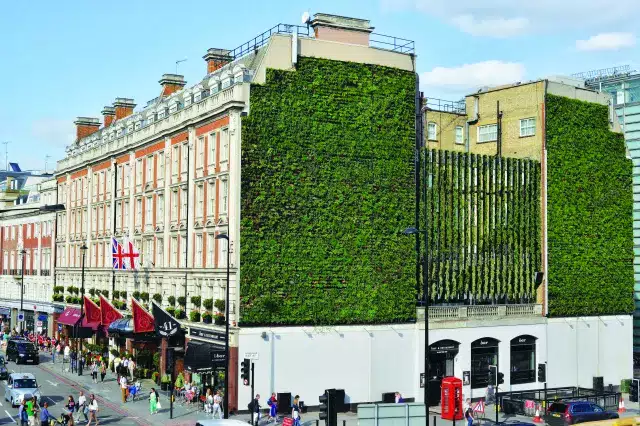



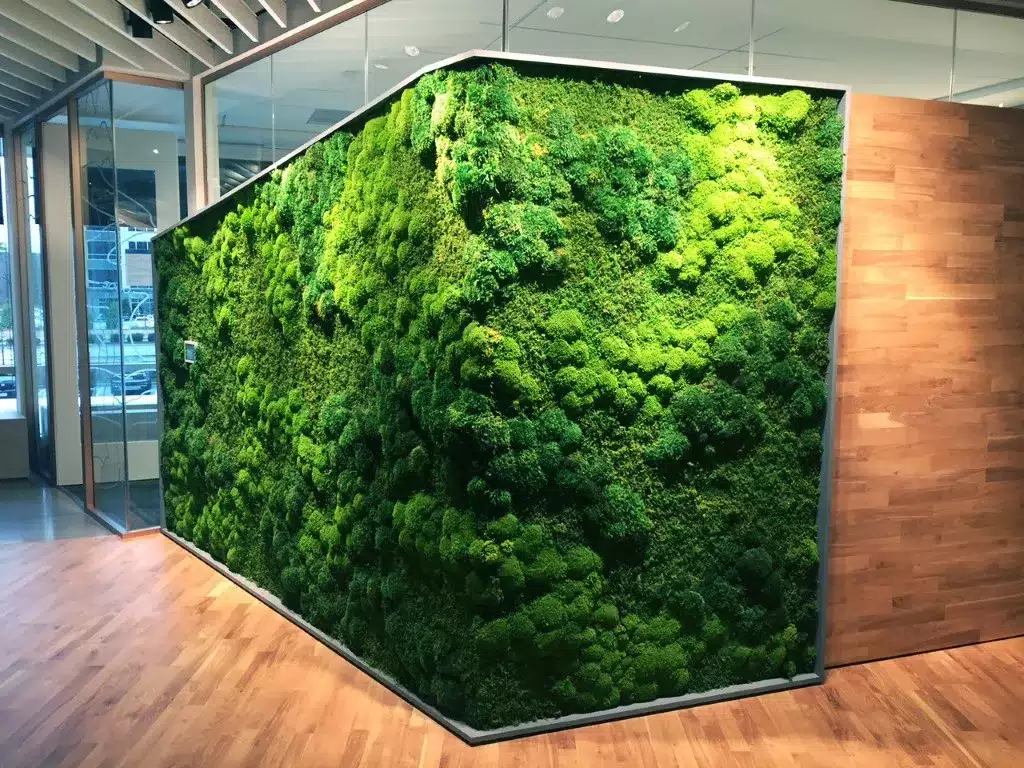
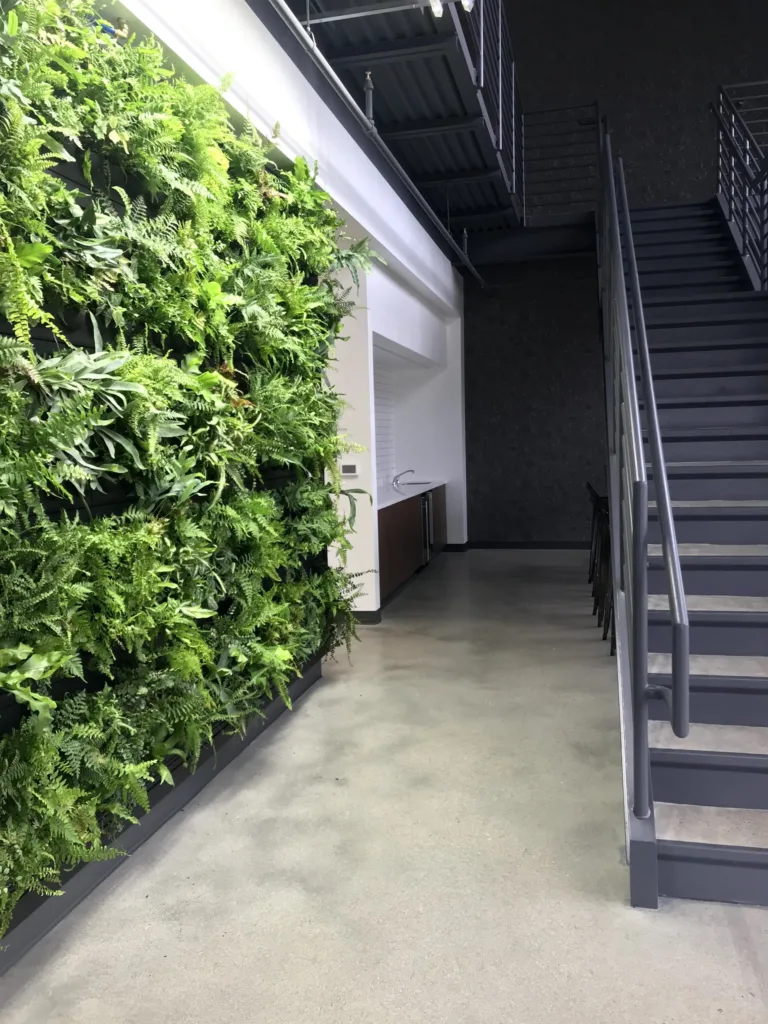
Living walls, also known as vertical gardens or green walls, are vertical structures covered with plants. They can be installed both indoors and outdoors and add a touch of greenery to walls and facades. Living walls also provide benefits such as improved air quality and noise reduction.
Plants in living walls act as natural air filters, removing pollutants and improving indoor air quality. They also help reduce noise levels by absorbing sound waves, creating a more peaceful and calm environment. Furthermore, living walls can contribute to the thermal regulation of buildings, reducing energy consumption and improving overall sustainability.
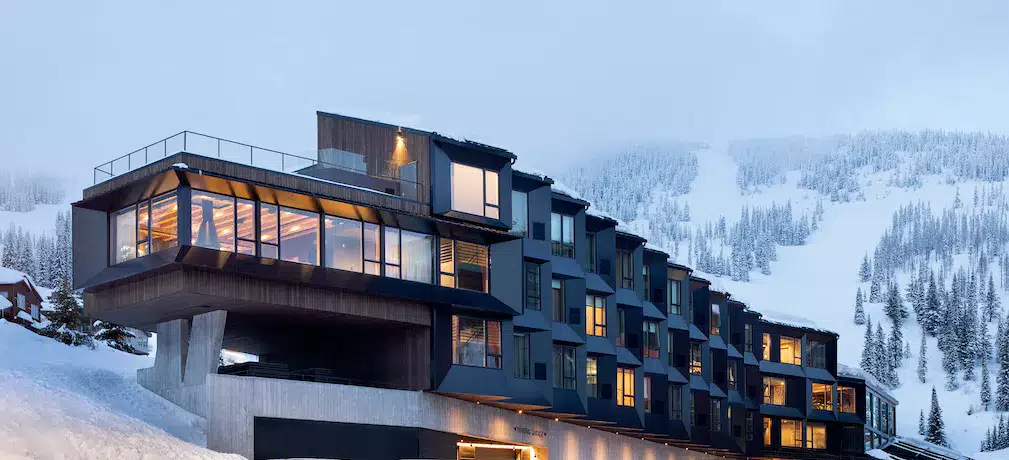
Plant-based Facades and Siding
Plant-based facades and claddings are another innovative approach to incorporating plants into building design. These systems involve the use of vegetative materials or systems that support the growth of plants on the exterior surfaces of buildings. They offer numerous benefits, including improved aesthetics, thermal regulation and reduced environmental impact.
Plant-based facades can be created using a variety of techniques, such as using climbing plants or installing modular systems that support plant growth. These facades not only add a natural and visually appealing element to buildings, but also provide thermal insulation, reducing the need for artificial cooling or heating systems.
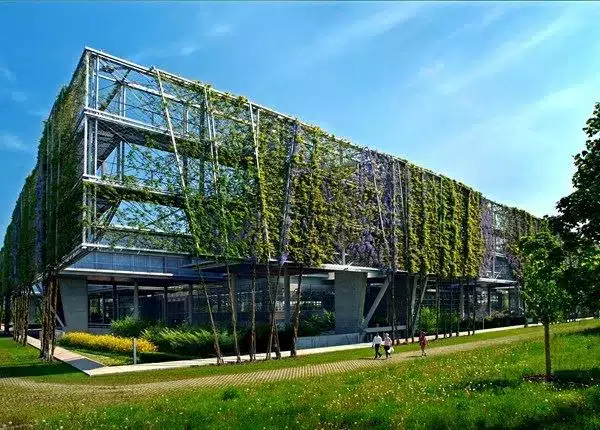
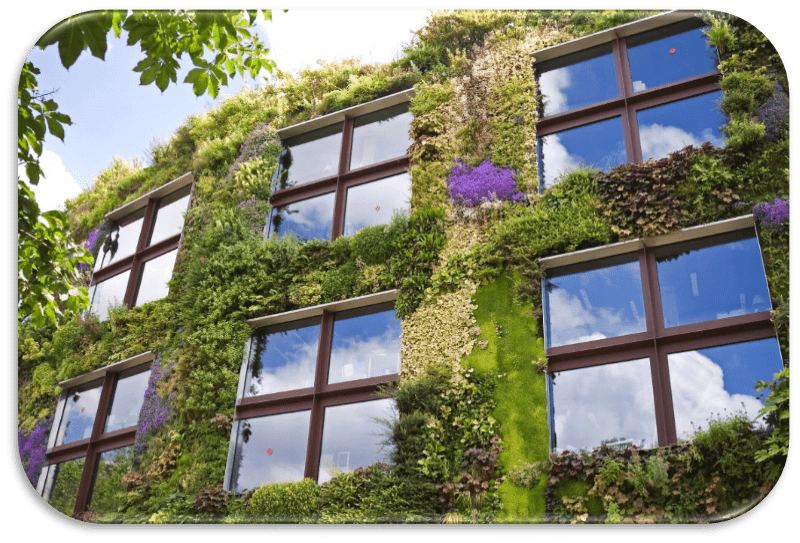


Exterior cladding systems that incorporate plants can also contribute to the sustainability of buildings. These systems often use materials such as recycled wood or plant-based fibers, reducing dependence on traditional building materials. In addition, the plants in these cladding systems help regulate temperature, improve air quality and provide habitat for wildlife.
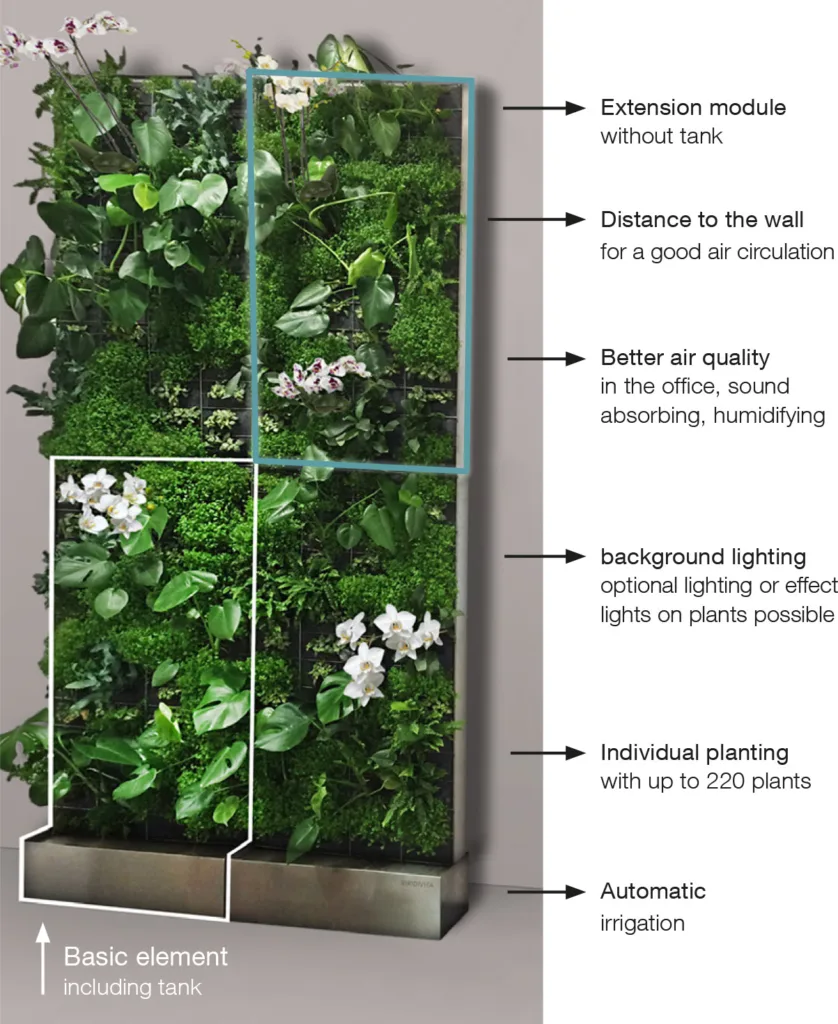
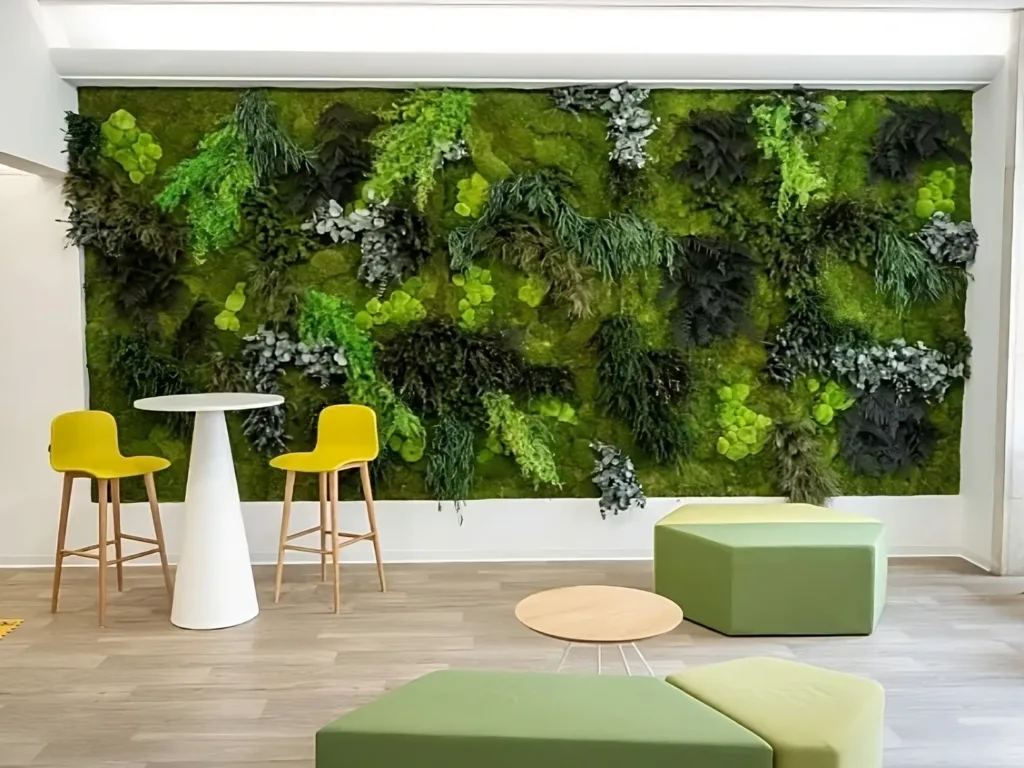
Indoor Planting and Landscaping
Indoor plant landscaping and landscaping involves the strategic placement of plants in the interior spaces of buildings. This practice not only enhances the visual appeal of the space, but also provides numerous benefits for building occupants, such as improved air quality, reduced stress and increased productivity.
Indoor plants act as natural air purifiers, removing pollutants and toxins from the air. This can help create a healthier indoor environment and reduce the risk of respiratory problems. Plants have also been shown to have a positive impact on mental well-being, reducing stress levels and improving mood and concentration.
Incorporating plants indoors can also improve acoustics by absorbing sound waves and reducing noise levels. This is particularly beneficial in open-plan offices or areas with high foot traffic. Furthermore, the presence of plants is a valuable addition to workspaces, increasing productivity and creativity.
Case Studies and Examples of Sustainable Plant-based Buildings
In the world of sustainable architecture, there are many successful examples of plant-based buildings that showcase the integration of plants into design. These buildings also emphasize their environmental and health benefits. In this article, we will examine some notable examples of plant-based buildings, discuss lessons learned and best practices, and explore future trends and innovations in sustainable plant-based building design.
Examples of successful plant-based buildings
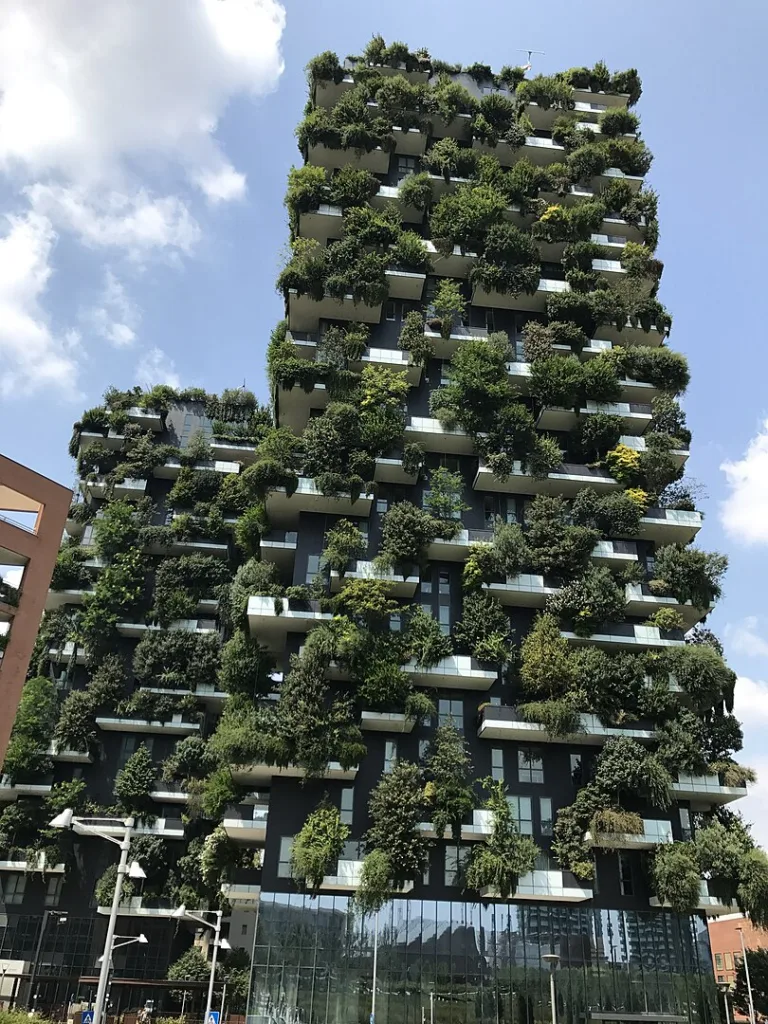
- Bosco Verticale, Milano, İtalya: Bitki temelli binaların en ikonik örneklerinden biri olan Bosco Verticale veya “Dikey Orman”, 900’den fazla ağaç ve 20.000 bitkiyle kaplı bir çift konut kulesidir. 2014 yılında tamamlanan bu proje Milano’nun hava kalitesini iyileştirmiş, enerji tüketimini azaltmış ve kuşlar ve böcekler için bir yaşam alanı sağlamıştır.
- One Central Park, Sydney, Avustralya: Ünlü mimar Jean Nouvel tarafından tasarlanan One Central Park, binanın yüksekliğine yayılan çarpıcı bir dikey bahçeye sahiptir. Bu yemyeşil alan kentsel ısı adası etkisini azaltarak ve hava kalitesini iyileştirerek binanın sürdürülebilirliğine de katkıda bulunuyor.
- The Edge, Amsterdam, Hollanda: The Edge, dış cephesinde yaşayan bir duvar içeren son derece sürdürülebilir bir ofis binasıdır. Bu yenilikçi tasarım doğal yalıtım sağlayarak ve yapay soğutma ihtiyacını azaltarak binanın enerji verimliliğine de katkıda bulunuyor.
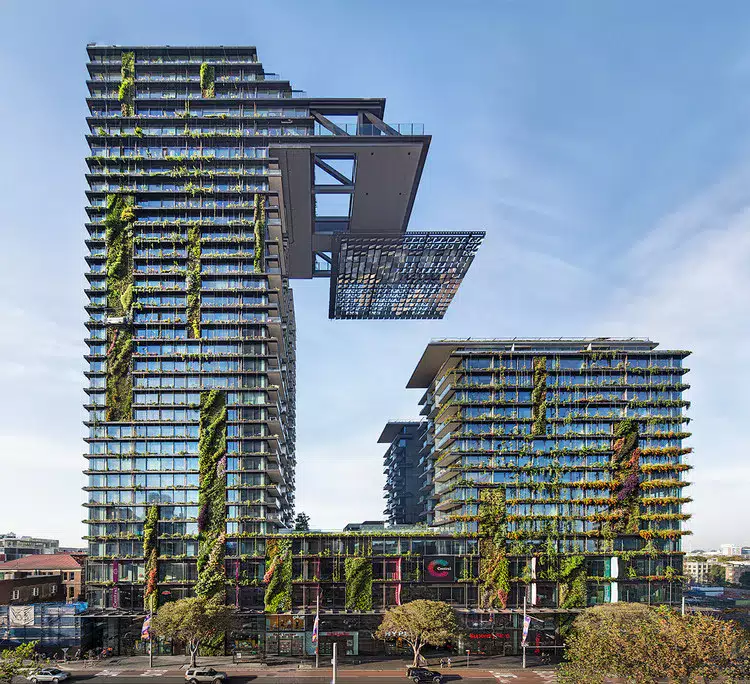
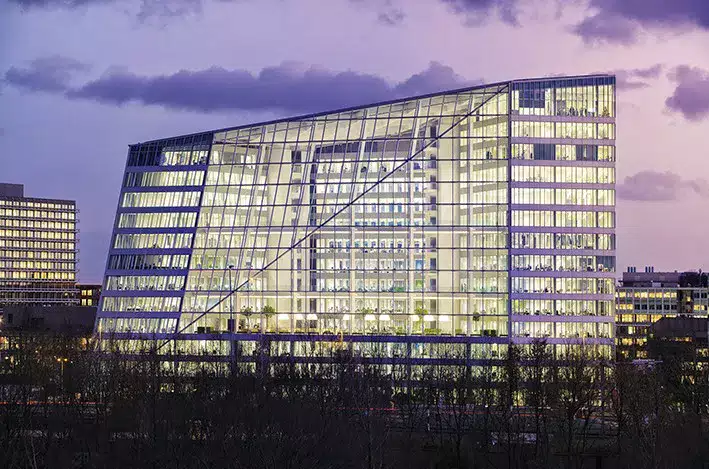



Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Many valuable lessons have been learned through the development and implementation of plant-based buildings, leading to the establishment of best practices in sustainable design. Some important lessons include:
- Bitkilerin Tasarım Aşamasından İtibaren Entegrasyonu: Bitkilerin bina tasarımına dahil edilmesi projenin ilk aşamalarından itibaren düşünülmelidir. Bu, yapısal destek, sulama sistemleri ve bakım gereksinimlerinin uygun şekilde planlanmasını sağlar.
- Uygun Bitki Türlerinin Seçimi: Yerel iklim ve çevre koşullarına uygun doğru bitki türlerinin seçilmesi, bitki temelli binaların uzun vadeli başarısı için çok önemlidir. Kuraklığa dayanıklı ve az bakım gerektiren bitkiler sıklıkla tercih edilir.
- İşbirliği ve Uzmanlık: Başarılı bitki temelli binalar mimarlar, peyzaj tasarımcıları, bahçıvanlar ve diğer uzmanlar arasında işbirliği gerektirir. Bu uzmanların bilgi birikimi ve uzmanlığı, tasarımın hem estetik açıdan hoş hem de çevresel açıdan sürdürülebilir olmasını sağlar.
- Bakım ve İzleme: Bir binadaki bitkilerin sağlığı ve canlılığı için düzenli bakım ve izleme şarttır. Bu, uygun sulama, budama ve haşere kontrolünü içerir. Bina sahipleri, yeşil unsurların uzun ömürlü olmasını sağlamak için sürekli bakım için kaynak ayırmalıdır.
Future Trends and Innovations in Sustainable Plant-based Building Design
As the field of sustainable architecture continues to evolve, several future trends and innovations in plant-based building design are emerging. These include:
- Biyofilik Tasarım: Biyofilik tasarım, doğa ile derin bir bağ kurmayı teşvik eden binalar yaratmayı amaçlar. Doğal ışık, yeşillik manzarası ve dış mekanlara doğrudan erişim gibi unsurları içerir. Bu yaklaşım sürdürülebilirliği de teşvik eder.
- Modüler Yeşil Sistemler: Önceden yetiştirilmiş paneller veya modüller gibi modüler yeşil sistemler, kurulum ve bakım kolaylıkları nedeniyle popüler hale gelmektedir. Bu sistemler tasarımda esneklik sağlar ve hem yeni hem de mevcut binalara kolayca entegre edilebilir.
- Dikey Tarım: Yerel kaynaklı gıdaya olan talebin artmasıyla birlikte dikey tarım ilgi görmeye başlamıştır. Dikey çiftlikler, mahsulleri kontrollü bir kapalı ortamda yetiştirmek için hidroponik veya aeroponik kullanır. Dikey çiftliklerin binalara entegre edilmesi, nakliye ve karbon emisyonlarını azaltırken taze ürün sağlayabilir.
- Akıllı Teknoloji Entegrasyonu: Akıllı teknolojinin bitki temelli binalara entegrasyonu, yeşil unsurların verimli bir şekilde izlenmesini ve yönetilmesini sağlar. Otomatik sulama sistemleri, bitki sağlığını izlemek için sensörler ve enerji tasarruflu aydınlatma sistemleri, bitki büyümesini ve sürdürülebilirliği optimize edebilen akıllı teknolojilere örnektir.
As a result, incorporating plants into building design provides numerous benefits for both the environment and the occupants. Successful examples such as Bosco Verticale, One Central Park and The Edge demonstrate the potential of plant-based buildings to transform urban landscapes while promoting sustainability. By learning from these examples, following best practices and embracing future trends and innovations, we can create buildings that contribute to a greener and healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What kind of plants are suitable for green roofs?
- Depending on the specific climate and environmental conditions, various plant species can thrive on green roofs. Some common plant choices include sedums, grasses and herbaceous perennials. It is important to choose plants that are drought tolerant, have shallow root systems and can withstand exposure to wind and sunlight.
- Can living walls be installed indoors?
- Yes, living walls can be installed indoors if the necessary conditions are met. Indoor living walls require proper lighting, irrigation systems and maintenance to ensure the health and vitality of the plants. It is important to consult experts or professionals in living wall installations to determine feasibility and suitability for interiors.
- How can plants improve indoor air quality?
- Plants improve indoor air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. They also have the ability to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants from the air. The leaves, stems and roots of plants act as natural filters, trapping and breaking down harmful substances.
- What are some popular plants for indoor plant landscaping?
- There are numerous plant options for indoor plant landscaping, depending on factors such as lighting conditions and maintenance requirements. Some popular choices include pothos, snake plants, peace lilies and spider plants. These plants are known for their ability to thrive in indoor environments and require minimal maintenance.
- How can plant-based facades and cladding contribute to sustainability?
- Plant-based facades and siding contribute to sustainability in several ways. First, they provide natural insulation, reducing the need for artificial cooling or heating systems. This helps to save energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, the plants in these systems help regulate temperature, creating a more comfortable and energy-efficient indoor environment.
- How often should I water my indoor plants?
- The frequency of watering for indoor plants depends on various factors such as plant type, pot size and environmental conditions. As a general guideline, it is best to allow the top inch of soil to dry before watering again. However, it is important to monitor the specific needs of each plant and adjust watering accordingly.
- Are there natural alternatives to chemical pesticides for pest control?
- Yes, there are various natural alternatives to chemical pesticides for pest control. These include the use of beneficial insects such as ladybirds or praying mantises, as well as the application of organic insecticidal soaps or moisture oil. In addition, physical barriers such as sticky traps or nets can also be effective in preventing pest infestations.
- How can I improve the long-term health of my plants?
- To support the long-term health of your plants, it is important to provide them with sufficient sunlight, water and nutrients. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests or disease and take appropriate action if necessary. Pruning and removing dead or damaged plant material can also help maintain plant health and encourage new growth.
- Can I use recycled materials for plant care?
- Yes, you can use recycled materials for plant care. For example, you can reuse plastic containers or bottles as plant pots or use recycled paper or cardboard as mulch.
- What are the best plant species to improve acoustic performance?
- Plants with large, broad leaves or dense foliage are particularly effective at absorbing sound. Some examples include Ficus elastica (Rubber Plant), Philodendron and Dracaena. However, any plant can contribute to sound absorption to some degree, so feel free to choose plants that suit your personal preferences and space.
- How many plants do I need to improve acoustic performance?
- The number of plants needed depends on the size of the space and the level of acoustic enhancement desired. As a general guideline, aim for at least one plant per 100 square feet of space. However, you can always add more plants if you feel that additional sound absorption is necessary.
- Can artificial plants provide the same acoustic benefits as real plants?
- While artificial plants offer some visual appeal, they do not provide the same acoustic benefits as real plants. The complex structure and living nature of real plants allows them to absorb and propagate sound more effectively. Therefore, for optimum acoustic performance, real plants are recommended.
- Can plants be used to reduce noise in outdoor spaces?
- Yes, plants can also be used to reduce noise outdoors. Trees, hedges and shrubs can act as natural barriers, blocking and absorbing sound from nearby roads or other sources. Also, incorporating plants into outdoor seating areas or patios can create a more peaceful and pleasant environment.
- Are there any maintenance considerations when using plants for acoustic performance?
- Plants need regular care and maintenance to thrive and continue to provide acoustic benefits. This includes watering, pruning and ensuring they receive adequate sunlight. It is important to choose the appropriate plants for the specific indoor or outdoor environment and follow proper care guidelines to keep them healthy and vibrant.
- How much time should I spend in nature to experience its mental health benefits?
- There is no set amount of time that guarantees the mental health benefits of nature. However, research shows that spending at least 120 minutes a week in nature can lead to significant improvements in mental wellbeing. This time can be broken down into smaller increments, such as 20 minutes a day.
- Can I experience the same benefits by looking at pictures or videos of nature?
- Looking at pictures or videos of nature can provide some relaxation, but it does not offer the same benefits as direct exposure to nature. The sensory experience of being in nature – feeling the breeze, smelling the flowers and hearing the sounds – is an important part of the therapeutic effect.
- What if I live in a city with limited access to natural areas?
- Even in urban environments, there are often opportunities to connect with nature. Explore local parks, botanical gardens or rooftop gardens. Bringing nature indoors through houseplants or nature-inspired artwork can also have a positive impact on mental wellbeing.
- Can nature therapy be used as a complementary treatment for mental health problems?
- Yes, nature therapy, also known as ecotherapy or green therapy, can be used as a complementary treatment for mental health issues. It can be especially beneficial for individuals with anxiety, depression or stress-related disorders. However, it is important to consult a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
- How can I include nature more in my daily life?
- There are many ways to incorporate nature into your daily life. Start by spending time outdoors, such as going for a walk, having a picnic or practicing yoga outdoors. Create a green space in your home or office with plants and natural elements. Take breaks throughout the day to go outside and get some fresh air. The important thing is to prioritize and make time for nature in your daily routine.
- How many plants do I need to improve indoor air quality?
- The number of plants needed to improve indoor air quality depends on factors such as room size and plant species used. As a general guideline, it is recommended to have at least one plant per 100 square feet of space. However, having more plants can provide more air purifying benefits.
- Can any plant improve indoor air quality, or are some more effective than others?
- While all plants contribute to air purification to some degree, some plants are more effective than others. Plants with larger leaves and more surface area, such as Peace Lily and Snake Plant, are known for their exceptional air purification abilities. When choosing plants, it is also important to consider the specific pollutants you want to target.
- Do plants require special care to thrive indoors?
- Most indoor plants are relatively low maintenance and can thrive in typical indoor conditions. However, it is very important to provide them with adequate light, water and occasional fertilization. Different plants have different care requirements, so it is best to research the specific needs of each plant you choose.
- Can plants help reduce odors indoors?
- Yes, plants can help reduce odors indoors. They can absorb and neutralize some volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to unpleasant odors. Plants such as Boston Fern and Areca Palm are particularly effective at removing odors from the air.
- Are plant-based materials as durable as traditional building materials?
- Yes, many plant-based materials such as bamboo, hemp concrete and cork are known for their durability. Bamboo in particular is incredibly strong and can rival the strength of traditional building materials such as wood and steel.
- Are plant-based insulation materials as effective as traditional insulation materials?
- Yes, plant-based insulation materials such as cellulose and sheep wool offer excellent thermal insulation properties. Just like traditional insulation materials, they can effectively regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption.
- Are low-VOC paints and varnishes available in a wide range of colors and finishes?
- Yes, low-VOC paints and varnishes come in a variety of colors and finishes and allow for endless design possibilities. You can achieve the look you want while prioritizing the health and well-being of the building’s occupants.
- Are plant-based materials more expensive than conventional materials?
- The cost of plant-based materials can vary depending on factors such as availability and location. In some cases, they can be slightly more expensive than traditional materials. However, the long-term benefits such as sustainability and improved indoor air quality often outweigh the initial cost.
- Can plant-based materials be recycled or reused at the end of their life cycle?
- Yes, many plant-based materials such as bamboo, cork and sheep wool are biodegradable and can be recycled or reused at the end of their life cycle. This further reduces their environmental impact and supports a circular economy.
- What are green roofs and how do they contribute to water savings?
- Green roofs are vegetated roofs that absorb rainwater and reduce stormwater runoff. They act as natural sponges, retaining rainwater and reducing the burden on municipal drainage systems. Green roofs also reduce the need for irrigation by using the captured rainwater for plant growth.
- Yağmur suyu hasadı nedir ve suyun korunmasına nasıl yardımcı olur?
- Yağmur suyu hasadı, yağmur suyunun daha sonra kullanılmak üzere toplanmasını ve depolanmasını içerir. Toplanan yağmur suyunu sulama gibi içilemez amaçlar için kullanarak belediye su kaynaklarına olan bağımlılığı azaltır. Bu, tatlı su kaynaklarının korunmasına yardımcı olur ve binalarda sürdürülebilir bir su döngüsünü teşvik eder.
- What is gray water recycling and how does it contribute to saving water?
- Graywater recycling is the process of treating and reusing water from sources such as sinks, showers and washing machines. By recycling graywater for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, water use can be minimized and freshwater resources can be conserved.
- What are efficient irrigation systems and how do they promote water saving?
- Efficient irrigation systems such as drip irrigation and smart controllers minimize water waste by delivering water directly to the plant’s root zone and adjusting irrigation schedules based on real-time data. These systems optimize water use, prevent overwatering and promote water conservation.
- How can architects and designers incorporate water-saving practices into sustainable building design?
- Architects and designers can incorporate water-saving practices by implementing green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, gray water recycling systems and efficient irrigation systems.
- How do plants contribute to energy efficiency in buildings?
- Plants contribute to energy efficiency in buildings through shading and insulation. Plants can be strategically placed around windows and facades to block direct sunlight and reduce the need for artificial cooling systems. Furthermore, the leaves of plants act as natural insulation, regulating indoor temperatures and reducing the load on heating and cooling systems.
- Can plants improve indoor air quality?
- Yes, plants can improve indoor air quality. They release oxygen through photosynthesis, which improves air circulation and quality. Plants also have the ability to absorb and filter harmful toxins such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and formaldehyde, thus creating a healthier indoor environment for building occupants.
- How do plants reduce energy consumption in buildings?
- Plants reduce energy consumption in buildings by providing natural shading, insulation and ventilation. By utilizing these natural elements, buildings can rely less on artificial heating, cooling and ventilation systems, resulting in lower energy use and lower utility bills.
- Are there any benefits of plants for building occupants?
- Yes, plants have numerous benefits for building occupants. Exposure to nature and greenery has been shown to reduce stress, improve mood and increase cognitive function. By incorporating plants into building design, sustainable buildings can improve the overall well-being and productivity of occupants.
- Are there specific plants recommended for sustainable building design?
- There are several plant species that are well suited for sustainable building design. Some popular choices include spider plants, peace lilies, snake plants and pothos. These plants are known for their ability to thrive indoors and improve air quality.