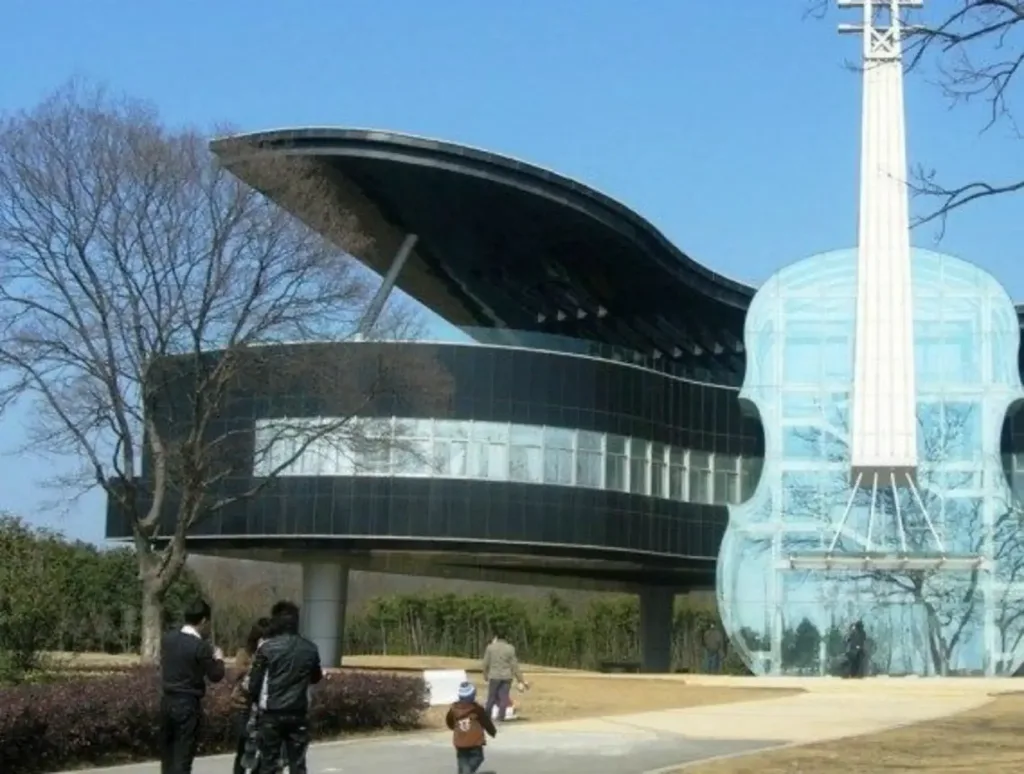
The Piano House is a remarkable architectural concept that creatively blends the world of music with structural design. Located around the world, these unique buildings capture the essence of music through their form and function.
- Location: The Piano House is located in Huainan, Anhui Province, China.
- Year of Completion: The building was completed in 2007.
- Architectural Firm: Designed by Huainan Institute of Architectural Design and Research.
- Unique Design: The structure is shaped like a grand piano and violin, symbolizing the harmony of music and architecture.
- Functionality: It serves as a showroom for a local real estate company and also as a cultural space.
- Materials Used: The building features a combination of glass, steel and concrete that reinforces its modern aesthetic.
- Cultural Significance: The Piano House represents the integration of art and architecture and reflects the cultural values of music in society.
- Visitor Experience: The interior features a staircase that resembles piano keys, creating an immersive experience for visitors.
- Environmental Considerations: The design incorporates large glass panels to maximize natural light and reduce energy consumption.
- Recognition: The Piano House has received international attention for its whimsical design and has been featured in various architectural publications.
Whether as a public space, a performance venue or a residence, the Piano House stands as a testament to how architecture can harmonize with art. This research explores the intricacies of the Piano House, its significance in contemporary architecture and the deeper connection between music and design.

Architectural Concept Overview
The Piano House is a creative structure that takes the shape of a grand piano and is often accompanied by other musical instruments. This architectural marvel also aims to evoke emotional responses through its design. The concept typically includes elements reminiscent of piano keys, musical notes and even the instrument itself, creating a playful yet purposeful environment. Such buildings often serve as cultural centers, inviting the public to engage with music and art in a spatially immersive way.
One of the most famous examples is the Piano House in Huainan, China, which features a grand piano structure and a giant violin. This design encourages interaction, allowing visitors to appreciate the beauty of music while exploring the building. The Piano House exemplifies how architecture can transcend traditional boundaries and encourage creativity and collaboration.
Significance in Contemporary Architecture
The Piano House represents a shift in contemporary architecture towards more expressive and conceptual designs. It combines artistic expression with functionality, challenging traditional notions of what a building should be. This approach reflects a broader trend in architecture where form and meaning are deeply intertwined. Architects today strive to create spaces that tell stories about culture, society and creativity.
The significance of the Piano House lies in the way it inspires discussions about the role of art in everyday life. As cities become more homogenized, structures like the Piano House stand out as beacons of creativity, encouraging people to interact with their environment in new and meaningful ways. They invite people to interact with the space in a dynamic way, reminding us that architecture can be a canvas for artistic exploration.
Location and Context
The location of a Piano House plays a crucial role in its design and reception. Often located in urban areas where artistic expression is celebrated, these buildings become integral parts of the cultural landscape. For example, the Piano House in Huainan is located in a vibrant community that values music and the arts, making it a fitting addition to the neighborhood.
Contextually, the Piano House serves as a focal point within its neighborhood. It invites passersby to pause, reflect and engage with the building and its surroundings. The architectural design often takes into account local culture, history and community needs, ensuring that the Piano House is in harmony with its context. This careful integration enhances the overall experience, making the building a valuable part of the community.
Architectural Vision and Goals
The vision behind Piano House is based on the desire to create a space that celebrates music while encouraging community engagement. The architects envision these buildings as places where people can come together, share experiences and explore their creativity. Their aim goes beyond aesthetics to inspire future generations to appreciate art and embrace their own creativity.
Architects often collaborate with musicians and artists during the design process, ensuring that the building reflects the essence of music. This collaborative approach enhances the functionality of the space, making it suitable for performances, workshops and community gatherings. The overarching goal is to create an environment that resonates with harmony and encourages individuals to express themselves freely in the context of music and architecture.
The Role of Music in Architecture
There is a deep relationship between music and architecture; both art forms are based on rhythm, harmony and space. The Piano House embodies this connection by showing how music can influence architectural design and vice versa. The physical structure of the building can evoke musical experiences, just as music can enhance the perception of space.
Incorporating musical elements into the architecture invites people to experience the building in a multi-sensory way. By creating acoustically rich environments that enhance performances, design can allow music to resonate through halls and engage audiences. This interplay between music and architecture leads to a greater appreciation of both art forms, highlighting how they can coexist and enrich human experiences.
Ultimately, the Piano House is much more than an architectural innovation; it is a celebration of the arts, a community center and a testament to the creative spirit. Its importance in contemporary architecture lies in its ability to inspire and stir emotions, reminding us of the power of music and design to shape our world.
Design Features of the Piano House
The Piano House is an extraordinary architectural marvel that creatively combines design and function. Located in Huainan, China, this unique structure also stands out for its thoughtful integration of space, materials and environmental considerations. Each design feature contributes to its overall character and purpose, making it a fascinating subject of study in contemporary architecture.
Exterior Design and Aesthetics
The exterior of the Piano House immediately attracts attention with its bold and playful design. Shaped like a grand piano, the building features a striking facade that showcases smooth lines and glossy surfaces reminiscent of polished piano keys. The design embodies the harmony of art and architecture, inviting passersby to wonder and interact.
The use of large glass panels enhances the aesthetics, allowing natural light to flood the interior while offering views of the surroundings. This transparency creates a sense of openness and connection with the outside world. The piano-shaped roof, complete with a stepped staircase resembling the keys of a piano, further emphasizes the playful yet elegant concept. The overall design reflects a commitment to creativity and makes the Piano House an iconic symbol of joy and inspiration.
Interior Layout and Functionality
The interior of the Piano House is as innovative as the exterior. The interiors are designed to be flexible and functional, catering to a variety of uses. The main floor contains typical spaces for exhibitions, performances and educational activities, reflecting the building’s purpose as a cultural center. The open floor plan allows for easy movement and adaptability, making the building suitable for different events and gatherings.
The interior design incorporates elements that reflect the theme of music; curved walls and flowing spaces create an atmosphere of rhythm and harmony. Each space has been carefully organized to encourage interaction and collaboration and strengthen the spirit of community. Natural materials and soft colors are used to create a warm and inviting environment, making visitors feel comfortable and engaged.
Material Use and Sustainability
Sustainability is the cornerstone of Piano House’s design philosophy. The building uses eco-friendly materials that minimize environmental impact while enhancing structural integrity. Locally sourced materials not only reduce transportation emissions, but also support the local economy.
Innovative construction techniques such as high-performance insulation and energy-efficient glazing are used to ensure energy efficiency. These features help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while reducing reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems. The building also incorporates green technologies such as rainwater harvesting and solar panels to promote sustainability and reduce its carbon footprint. This commitment to eco-conscious design reflects a growing trend towards responsible and sustainable building practices in architecture.
Innovative Structural Elements
The structural elements of the Piano House are a testament to modern engineering and design innovation. The unique shape of the building poses challenges that architects and engineers have creatively solved. For example, the curved roof of the grand piano requires advanced structural support that showcases the ingenuity of contemporary construction techniques.
In addition to aesthetic appeal, these structural innovations ensure durability and safety. The use of lightweight materials where possible helps to reduce the overall load on the foundation, while the integration of advanced architectural software allows for precise calculations and simulations during the design phase. This blend of art and science exemplifies how modern architecture is pushing boundaries and exploring new possibilities in building design.
Integration with the Environment
One of the most commendable aspects of the Piano House is its careful integration with its surroundings. Set within a landscaped area, the building harmonizes with its natural surroundings rather than overpowering them. The design includes open spaces with gardens and pathways that encourage visitors to explore and connect with nature, enhancing the overall experience.
The Piano House also serves as a cultural landmark that encourages social interaction. It hosts a variety of events, performances and exhibitions that invite local residents and visitors to engage with the arts. This community focus not only enriches the cultural fabric of Huainan, but also reinforces the idea that architecture can be a catalyst for social connection and collaboration.
In summary, the design features of Piano House demonstrate a harmonious blend of creativity, functionality and sustainability. From its striking exterior to its innovative interiors, each element contributes to a building that serves as a meaningful space for community engagement. This architectural gem stands as a testament to the potential of design to inspire and connect people through art and culture.
Architectural Style and Influences
Architecture is a living expression of culture, history and innovation. Every building tells a story, influenced by the time it was built, the people who designed it and the environment in which it sits. This chapter explores the multifaceted nature of architectural style and the various influences that have shaped it, from modernism to local traditions.
The Influence of Modernism
Modernism emerged in the early 20th century as a reaction against traditional architectural styles. It emphasized simplicity, functionality and the use of new materials such as steel and glass. The movement sought to break free from historical constraints and embrace the future, reflecting the rapid changes in society.
Among the key concepts is the idea that form should follow function, meaning that the design of a building should be dictated by its intended use rather than ornamental concerns. This led to the creation of minimalist structures characterized by clean lines, open spaces and a lack of unnecessary decoration. Iconic examples such as the Bauhaus school and Le Corbusier’s Villa Savoye embody these principles and demonstrate how modernism transformed architectural practice.
In real-world applications, modernist buildings often serve as cultural landmarks and represent a shift towards progressive values in urban planning. From New York to Tokyo, cities around the world have modernist skyscrapers that redefine their skylines and symbolize innovation and economic growth.
Combining Cultural Elements
Architecture is a reflection of cultural identity and many buildings incorporate elements that reflect local heritage. This fusion of architectural styles often results in striking designs that celebrate a community’s history and traditions.
For example, in regions where indigenous cultures thrive, architects can use local materials, colors and motifs to create structures that honor their heritage. A striking example is the Sydney Opera House, which, despite its modern structure, evokes the sails of traditional boats, linking the building to Australia’s maritime history.
Cultural influences extend beyond aesthetics; they often inform the functionality of spaces. For example, many Asian cultures incorporate outdoor spaces and gardens into the design of homes, reflecting a deep connection with nature. By integrating cultural elements, architects create buildings with deep meaning for the communities they serve.
Comparison with other Iconic Buildings
When studying architectural styles, comparisons with iconic buildings provide valuable insights into how different influences shape design. Buildings such as the Eiffel Tower in Paris and the Taj Mahal in India illustrate how context, materials and cultural significance can lead to very different outcomes.
The Eiffel Tower, an iron lattice structure, was born out of the industrial revolution, symbolizing technological progress. Its unique design sparked controversy but ultimately became a beloved landmark that redefined the Paris skyline. In contrast, the Taj Mahal, built of white marble and decorated with intricate carvings, represents a different set of values, focusing on beauty, spirituality and monumentalization.
These structures tell overlapping yet different stories of their respective cultures, showing how architecture can serve as a canvas for human expression. By comparing such structures, we can appreciate the different paths architecture can take, shaped by local influences and global ideas.
Artistic Inspirations of Designers
Architects are often inspired by various art forms, from painting and sculpture to music and literature. This cross-pollination of ideas can lead to innovative designs that transcend traditional architectural boundaries.
For example, Frank Lloyd Wright’s inspiration from Japanese art and architecture is evident in his use of natural materials and integration of buildings with their surroundings. His design philosophy, known as “organic architecture”, emphasized the harmony between the building and its surroundings, resulting in iconic works such as Fallingwater.
Similarly, Zaha Hadid’s fluid, futuristic designs reflect a deep engagement with contemporary art and technology. Her work often blurs the lines between architecture and sculpture, creating dynamic spaces that challenge traditional forms. These artistic inspirations invite viewers to experience the buildings as works of art in their own right.
The Impact of Local Traditions on Design
Local traditions play a crucial role in shaping architectural styles and often dictate the materials used, construction techniques and overall aesthetics. In many regions, traditional construction methods have been passed down through generations, creating a sense of continuity and cultural identity.
In the Mediterranean, for example, the use of terracotta tiles and plaster reflects a climate-sensitive approach to architecture. These materials not only provide insulation, but also connect buildings to the landscape, creating a harmonious environment. In contrast, adobe structures in the American southwest show how indigenous communities have adapted to their environment and used local earth materials to create homes that adapt to the arid landscape.
The influence of local traditions also extends to social spaces. In many cultures, public squares and marketplaces are designed to encourage social interaction, reflecting values of community and cooperation. By honoring these traditions, architects ensure that their designs resonate with the people who live in them, creating spaces that are both functional and culturally significant.
As a result, the interplay of various influences in architecture results in a rich tapestry of styles and designs. By understanding these influences, from modernism and cultural elements to artistic inspirations and local traditions, we can appreciate architecture as a profound expression of human experience and creativity.
Engineering Challenges and Solutions
The field of engineering is inherently complex, marked by a constant evolution of challenges and the innovative solutions that emerge to meet them. As we explore the various dimensions of engineering challenges, we will reveal how professionals in the field confront obstacles such as structural integrity, environmental sustainability, site-specific dynamics, collaborative endeavors, and future flexibility. Each of these areas also emphasizes the importance of adaptive thinking in modern architecture.
Structural Engineering Innovations
Structural engineering is at the forefront of innovation, constantly evolving to create durable buildings. One of the most significant innovations in this field is the use of advanced materials such as carbon fiber and reinforced concrete. These materials offer greater strength without adding excess weight, enabling bold designs once thought impossible. For example, using lightweight materials in tall buildings can reduce the overall load on foundations, making them safer and more efficient.
Another exciting development is the integration of digital technology into the design process. Building Information Modeling (BIM) allows engineers to create detailed 3D models that simulate how structures will behave under various conditions. This technology helps identify potential weaknesses early in the design phase, enabling engineers to develop solutions before construction begins. The use of drones for site inspections and monitoring is also becoming commonplace, providing real-time data that can inform design adjustments.
These innovations also enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings, allowing architects to push the boundaries of creativity while ensuring safety and robustness.
Environmental Considerations
In an era where climate change poses significant challenges, engineers are increasingly focusing on environmental considerations in their projects. Sustainable design principles have become important, guiding the creation of structures that minimize the ecological footprint. An important approach is the use of green materials such as bamboo and recycled steel, which reduce the environmental impacts associated with traditional construction materials.
Energy efficiency has also come to the fore. Engineers are now tasked with designing buildings that utilize renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. This change is also helping the environment by reducing carbon emissions. One of the best examples is Bosco Verticale in Milan, Italy, a dual residential tower that integrates thousands of trees and plants into its design, improving air quality and promoting biodiversity.
Water management is another critical aspect of environmental engineering. Innovative solutions such as rainwater harvesting systems and permeable pavements help manage rainwater effectively, reducing runoff and minimizing flood risk. Such initiatives demonstrate how engineering can harmonize with nature and create sustainable urban environments.
Addressing Site Specific Challenges
Each construction site presents unique challenges influenced by geography, climate and existing infrastructure. Addressing these site-specific challenges requires a deep understanding of the local context. For example, buildings in earthquake-prone areas must be designed to withstand seismic forces using flexible foundations and shock-absorbing materials. Engineers often use advanced simulation techniques to predict how structures will respond to such natural events.
In coastal areas, rising sea levels pose a significant threat. Engineers should consider flood-resilient designs that elevate structures and incorporate breakwaters and levees to protect against storm surges. The design of the Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority’s projects exemplifies this approach, focusing on resilience in the face of climate change.
Furthermore, urban environments often present the challenge of limited space. By creatively using vertical space, engineers design high-rise buildings that maximize land use while adhering to safety regulations. Incorporating green roofs and vertical gardens also improves the urban ecosystem.
Collaborations with Engineers and Artists
The intersection of engineering and art is a powerful space for creativity and innovation. Collaborations between engineers and artists bring a new dimension to architectural design, where aesthetics and functionality coexist harmoniously. This partnership can lead to the creation of iconic structures that are also visually striking.
A notable example is the Sydney Opera House, where architect Jørn Utzon’s visionary design required innovative engineering solutions to realize the unique sail-like roof structure. Engineers and artists worked hand in hand to ensure that the building could withstand harsh coastal conditions while maintaining its artistic integrity.
In modern projects, these collaborations often involve the use of interactive installations that respond to environmental stimuli and engage the public in new ways. Such projects demonstrate how engineering can enhance the human experience in public spaces, encouraging community interaction and strengthening a sense of belonging.
Future-proofing the building
Looking to the future, engineers face the critical task of future-proofing structures against unforeseen challenges. This involves not only considering current environmental factors, but also anticipating future technological developments and societal changes. Flexible design is key; structures must be adaptable to accommodate changes in use, such as the conversion of commercial spaces into residential units as urban demographics evolve.
Incorporating smart technologies into building designs is another important aspect of future-proofing. Smart buildings equipped with sensors monitor energy use, environmental conditions and safety, allowing real-time adjustments that improve efficiency and security. The Edge in Amsterdam, often cited as one of the world’s greenest buildings, exemplifies this approach, integrating the latest technology to optimize energy consumption.
Moreover, resilience to climate impacts is becoming increasingly vital. Engineers are now focusing on creating structures that can withstand extreme weather events, incorporating features such as storm-resistant windows and raised foundations. This proactive mindset also ensures the safety and well-being of future residents.
In conclusion, the field of engineering challenges is broad and multifaceted and requires a mix of innovation, collaboration and forward-thinking strategies. By embracing these principles, engineers not only solve today’s challenges, but also pave the way for a sustainable and resilient architectural future.
Cultural and Social Impact
Architecture is more than the physical structures that define our cities; it plays an important role in shaping cultural identities and fostering social connections. The influence of buildings and spaces can reach far beyond their walls, affecting the way communities relate to each other, foster creativity and attract visitors. This chapter examines the multifaceted cultural and social impact of architecture, particularly through the lens of iconic buildings such as the Piano House.
Community Engagement and Reactions
When a community receives a new building, it often becomes a focal point for engagement and interaction. The Piano House, designed to resemble a giant piano and violin, is a perfect example. Its unique design attracts the curiosity of local residents and visitors alike.
As people gather around such landmarks, they participate in a shared experience that fosters a sense of belonging and identity. Community reactions can range from excitement and pride to skepticism and opposition. These reactions often lead to conversations within the community about the purpose and function of the building. By encouraging dialogue, it can act as a catalyst for community engagement, sparking discussions about architecture, urban planning, sustainability and the future of public spaces.
Role in Promoting Arts and Education
Architecture has the power to enhance the cultural fabric of a society by promoting art and education. The Piano House is also a venue for various cultural activities. It frequently hosts concerts, art exhibitions and educational workshops, turning it into a vibrant center for creativity.
By providing a space for artists and educators to collaborate, such buildings can inspire young minds and nurture local talent. Schools and community groups often use these spaces for educational programs, fostering a love of art among students. When architecture embraces opportunities for artistic expression and education, it helps foster a culturally rich environment that empowers individuals and strengthens community ties.
Impact on Local Tourism
Iconic structures such as the Piano House can significantly boost local tourism. Tourists are often attracted to unique architectural designs that offer a glimpse into the cultural identity of a place. The Piano House also attracts visitors with the experiences it offers.
Local businesses benefit from increased foot traffic as tourists explore the area, eat in nearby restaurants and shop in local stores. This influx of visitors can lead to economic growth, creating jobs and supporting small businesses. Moreover, showcasing local culture through architecture can enhance the appeal of communities as tourist destinations and encourage visitors to explore beyond typical attractions.
Events and Activities Organized at the Piano House
The Piano House is more than a visual marvel; it serves as a vibrant venue for a variety of events and activities. The venue is designed to host a wide range of gatherings, from music festivals to art fairs. These events not only provide entertainment, but also foster community spirit and collaboration.
For example, local musicians can perform in open spaces, inviting community members to join in celebrations of music and creativity. Workshops and lectures could be organized to engage the public in discussions about architecture, art and cultural heritage. By hosting a variety of events, the Piano House becomes a dynamic space that reflects the interests and passions of the community, making it a valuable asset.
Long-term Legacy and Preservation
As societies develop, the long-term legacy of architectural landmarks becomes increasingly important. The Piano House, with its distinctive design and cultural significance, represents a commitment to the preservation of local identity. Over time, such buildings can become symbols of resilience and continuity, reminding future generations of their cultural heritage.
Conservation work often involves community involvement and ensures that the building remains relevant and accessible. This collaborative approach also strengthens its role as a community center. Communities that invest in the preservation of culturally significant buildings affirm their connection to the past and inspire future generations to care for their cultural landscape.
Ultimately, the cultural and social impact of architecture is profound and multifaceted. Buildings like the Piano House exemplify how thoughtful design can foster civic engagement, support arts and education, enhance tourism, host a variety of events, and provide long-term legacy and preservation. Through these elements, architecture becomes a living part of society, enriching lives and shaping identities for years to come.
Future Prospects
As we conclude our exploration of architectural innovation, it is important to reflect on the journey we have taken. The dynamic field of architecture also affects our emotional and cultural experiences. The following sections will summarize the key insights from our discussions, highlight ongoing developments and anticipate the future of architectural endeavors. We will also discuss the importance of art in architecture and conclude with reflections on one of the most inspiring examples, the Piano House.
Summary of Key Takeaways
Throughout our research, we uncovered the multifaceted nature of architecture and revealed the interplay between functionality, aesthetics and context. One of the key realizations is that architecture is about creating spaces that resonate with their surroundings and the people who use them. We discussed how sustainable practices have become an integral part of modern design, highlighting the importance of environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies. Furthermore, the role of technology in architecture has transformed design processes, enabling architects to visualize and test their ideas in ways that were once unimaginable.
Ongoing Developments and Projects
The architectural landscape is constantly evolving with numerous projects pushing the boundaries of traditional design. Cities around the world are embracing innovative concepts such as vertical gardens and smart buildings that integrate advanced technology for enhanced living experiences. For example, the Bosco Verticale in Milan stands as a testament to combining nature with urban living, showing how residential buildings can contribute to biodiversity. In addition, global efforts to create structures that are resilient to climate change emphasize a commitment to future-proofing our cities. These ongoing projects are paving the way for new architectural paradigms.
Vision for Future Architectural Work
Looking to the future, the vision of future architecture is one of inclusivity, sustainability and technological integration. Architects are increasingly considering the social impact of their designs, seeking to create spaces that encourage community interactions and cultural expressions. The concept of biophilic design, which encourages the connection between humans and nature, is likely to become more prominent, promoting mental wellbeing and environmental stewardship. Furthermore, advances in artificial intelligence and virtual reality will enable architects to design more efficiently and interactively, allowing for greater collaboration and creativity. This forward-thinking approach will redefine how we perceive and inhabit our spaces.
The Importance of Art in Architecture
Art and architecture are intrinsically linked and each enriches the other in profound ways. A building’s aesthetics can evoke emotions, tell stories and reflect cultural identities. From sculptures integrated into facades to murals that enliven urban spaces, artistic elements enhance our engagement with architecture. Moreover, public art installations can encourage community engagement by transforming ordinary spaces into culturally significant landmarks. The Piano House, with its whimsical design inspired by musical instruments, exemplifies how art can go beyond mere function to invite wonder and joy. This integration emphasizes the importance of creativity in creating raw spaces.
Final Thoughts on the Piano House
The Piano House is an extraordinary example of what can happen when architecture meets artistic vision. Its design invites exploration and interaction, encouraging visitors to engage with their surroundings in a playful way. This building reminds us that architecture is not static, but can be a living, breathing entity that reflects the vitality of life around it. As we think about the future of architecture, let us be inspired by such innovative examples, envisioning spaces that foster creativity, sustainability and a deeper connection to our communities. As we celebrate the beauty of architectural art, we pave the way for a more harmonious and rich future.
FAQ
1. What is the Piano House?
The Piano House is a uniquely designed building in Huainan, China, in the shape of a grand piano and violin, symbolizing the blending of music and architecture.
2. When was the Piano House completed?
The building was completed in 2007.
3. Who designed the Piano House?
It was designed by the Huainan Institute of Architectural Design and Research.
4. What is the primary function of the Piano House?
It serves as a showroom for a local real estate company and a cultural space for community events.
5. What materials were used in the construction of the Piano House?
The building uses a combination of glass, steel and concrete to create its modern aesthetic.
6. What makes the Piano House culturally significant?
It represents the integration of art and architecture and emphasizes the cultural importance of music in society.
7. What unique features await visitors inside the Piano House?
The interior features a staircase designed to resemble piano keys, providing an immersive experience for visitors.
8. How does the Piano House incorporate environmental considerations?
The design uses large glass panels to maximize natural light, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability.
9. Has the Piano House received any recognition?
Yes, it has received international attention and has been featured in various architectural publications for its innovative design.
10. Can the public visit the Piano House?
Yes, visitors can explore the building and enjoy its unique architectural features.
Reflections on the Piano House
The Piano House in Huainan is an extraordinary architectural masterpiece that harmoniously blends music and design. Completed in 2007, this unique structure has become an iconic symbol of creativity in the region, mesmerizing with its grand piano and violin shape. Every detail reflects the innovative spirit of the architects and shows how architecture can resonate with cultural themes.
The building also functions as a cultural space celebrating the importance of music in society. The interior design, with a staircase reminiscent of piano keys, enhances the visitor experience, inviting them into a world where art and architecture merge.
This architectural marvel stands as a testament to modern design, emphasizing sustainability through the extensive use of glass for natural lighting. The Piano House is more than just a building; it represents a bold vision of what contemporary architecture can achieve.
What are your thoughts on the Piano House? Do you think its design effectively captures the essence of music and creativity? Is there a particular aspect of the building that resonates with you? We invite you to share your views.
Architect: Huainan Institute of Architectural Design and Research
Architectural Style: Modern
Year: 2007
Location: Huainan, Anhui Province, China
Discover more from Dök Architecture
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.